3D Whole Cell Model of a Mycoplasma Bacterium
Images by Martina Maritan
These illustrations show a model of an entire Mycoplasma genitalium cell. The model was created by Martina Maritan and Ludovic Autin at Scripps Research in the laboratory of Arthur J. Olson and David S. Goodsell. The protein concentration, length of DNA and mRNA, location of RNA polymerase and other DNA-binding proteins in the nucleoid, and location of ribosomes translating mRNA have been derived from computational simulations of a wild-type M. genitalium cell by Jonathan Karr and Markus Covert.
This snapshot represents a Mycoplasma cell at the beginning of its life cycle. Cell shape has been approximated to a sphere with a radius of ~145nm. Each protein is represented by a 3D structure coming from either homology modeling, a previous model of mycoplasma cytoplasm, experimental data, or homologues from the Protein Data Bank. The nucleoid structure was modeled with LatticeNucleoid. Small molecules, ions, and water are not shown in the illustrations, and would fill the spaces between the macromolecules. Different clipping planes and coloring schemes have been applied to the model to highlight specific areas/elements of the cell.
Detailed descriptions of the data curation, model building, and visualization methods can be found in the Journal of Molecular Graphics article: ‘Building Structural Models of a Whole Mycoplasma Cell’, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167351
These illustrations are freely available for use under a CC-BY-4.0 license. Right-click on the image to download the full-size image.
When you use these illustrations, please include the attribution: “Image by Martina Maritan, Scripps Research.”

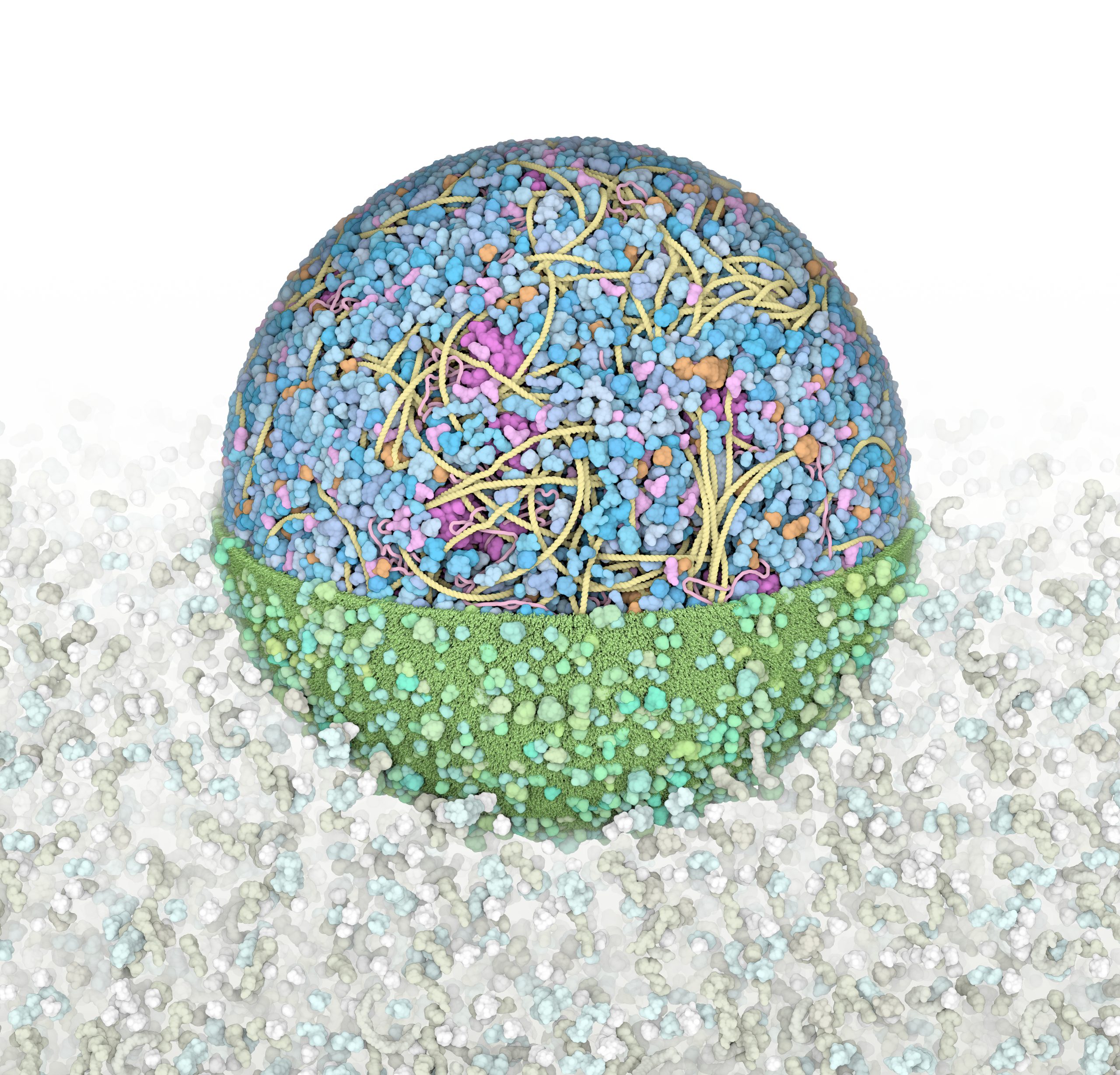
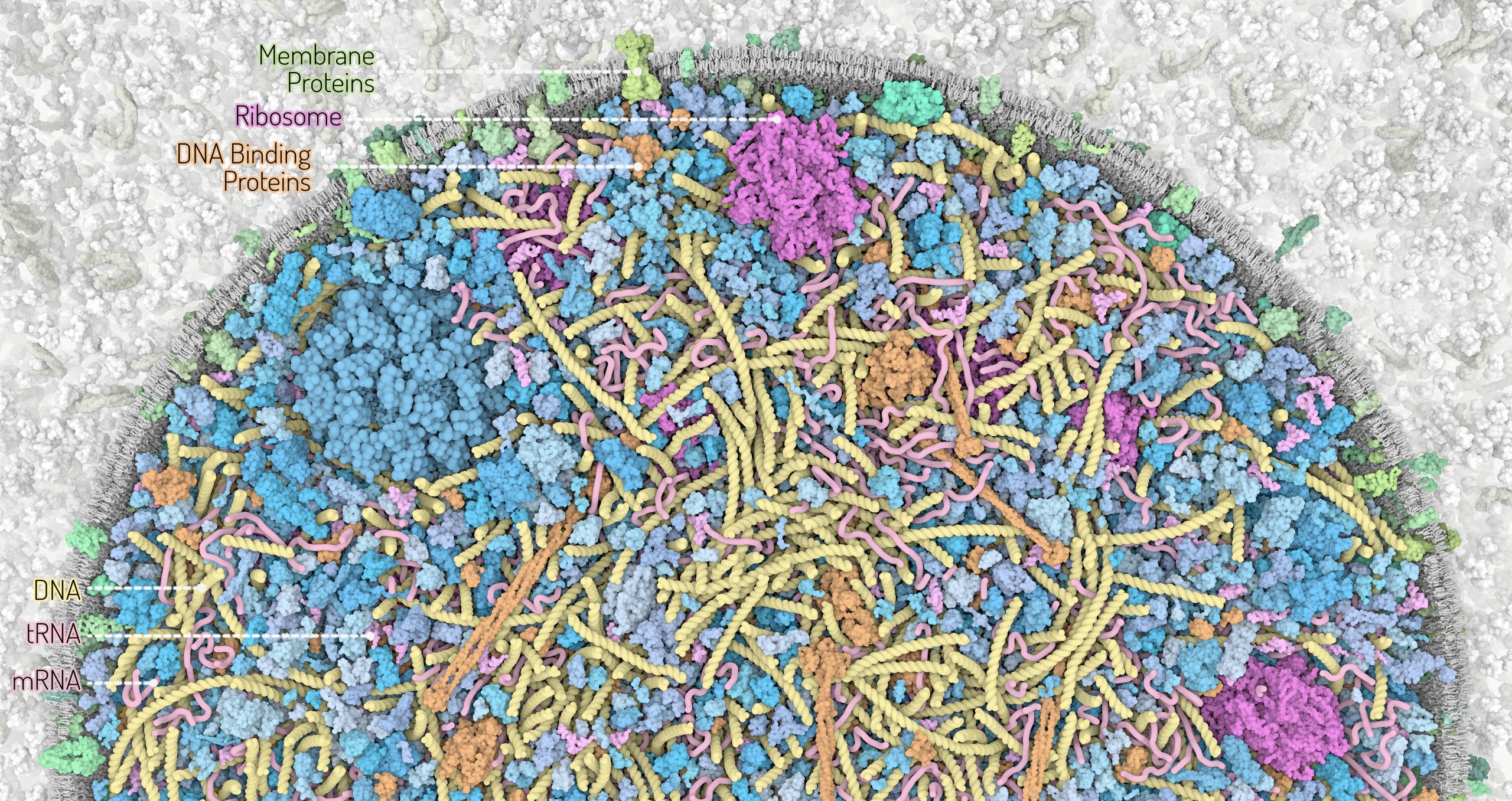
3D Whole Cell (3D-WC) model of a Mycoplasma genitalium cell
Horizontal clipping planes view
The 3D-WC model of Mycoplasma genitalium visualized with CellPACKgpu. Two clipping planes progressively hide parts of the model. The upper section highlights ribosomes (magenta), DNA (yellow) and mRNA (pink) filaments; the central section shows the bacterial nucleoid in the context of soluble macromolecules (DNA binding proteins in orange, cytoplasmic proteins in shades of blue, tRNAs in bright pink); the lower section shows the cell membrane (grey/green) with associated membrane proteins (shades of green).
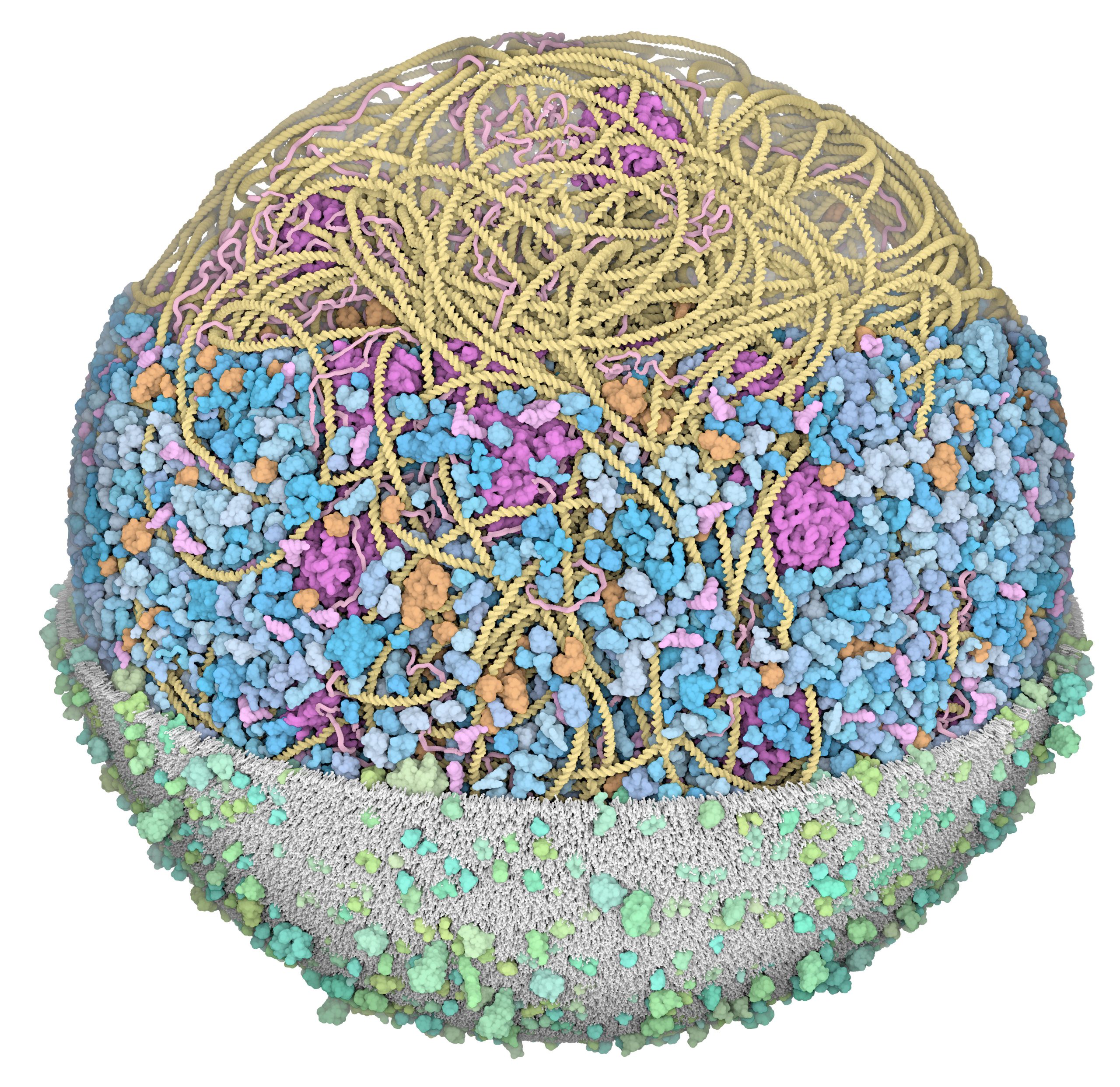
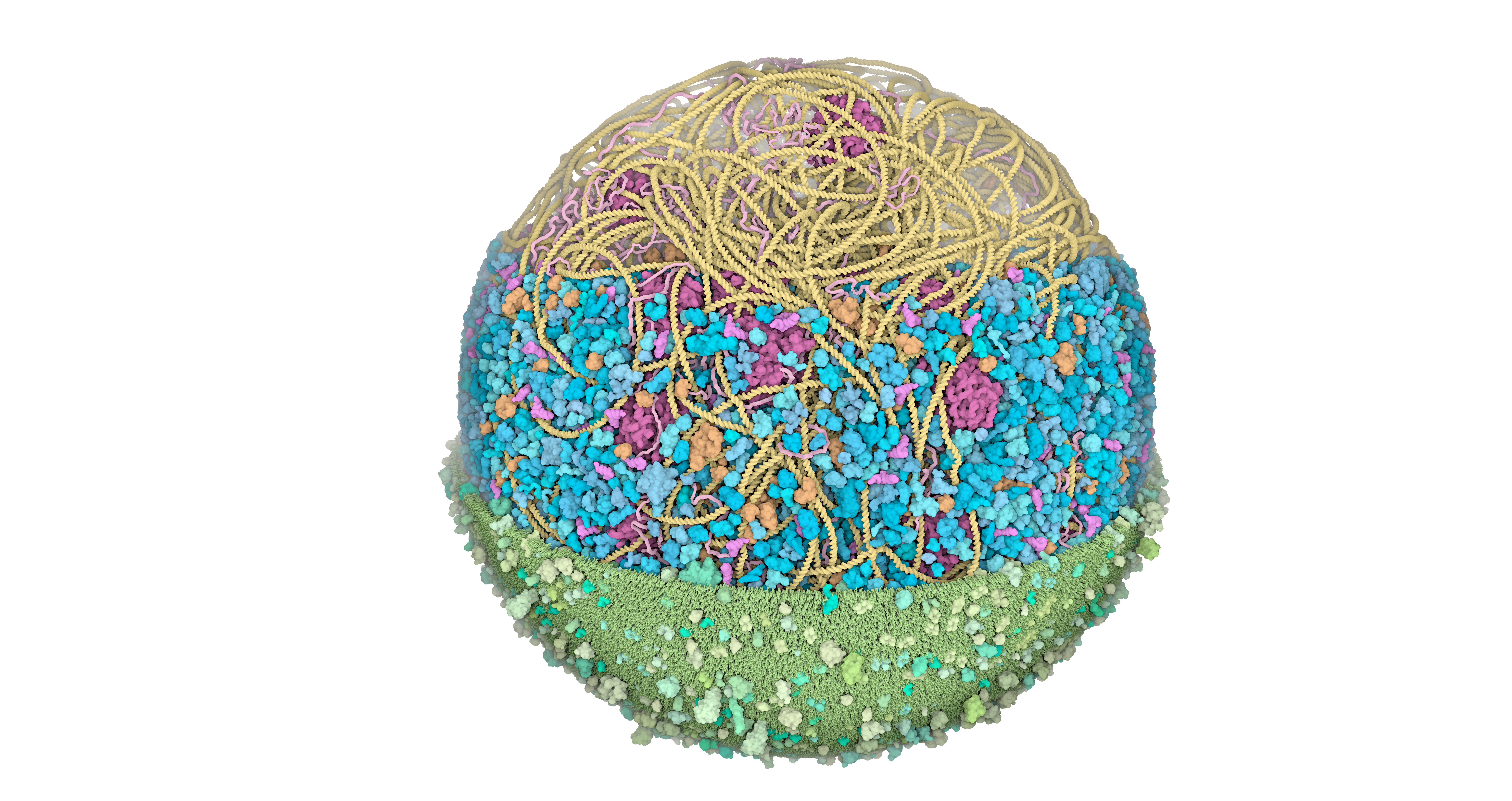
large file in png format with a transparent background
3D Whole Cell (3D-WC) model of a Mycoplasma genitalium cell
Vertical clipping plane view
The 3D-WC model of Mycoplasma genitalium visualized with CellPACKgpu. A vertical clipping plane hides parts of the model and exposes the bacterial nucleoid model and associated proteins. Left: ribosomes (magenta), DNA binding proteins (orange), DNA (yellow) and mRNA (pink) filaments. Right: 3D-WC model with a horizontal clipping plane that shows the nucleoid and soluble macromolecules on top (cytoplasmic proteins in shades of blue, tRNAs in bright pink) and the cell membrane (grey) with associated membrane proteins (shades of green).
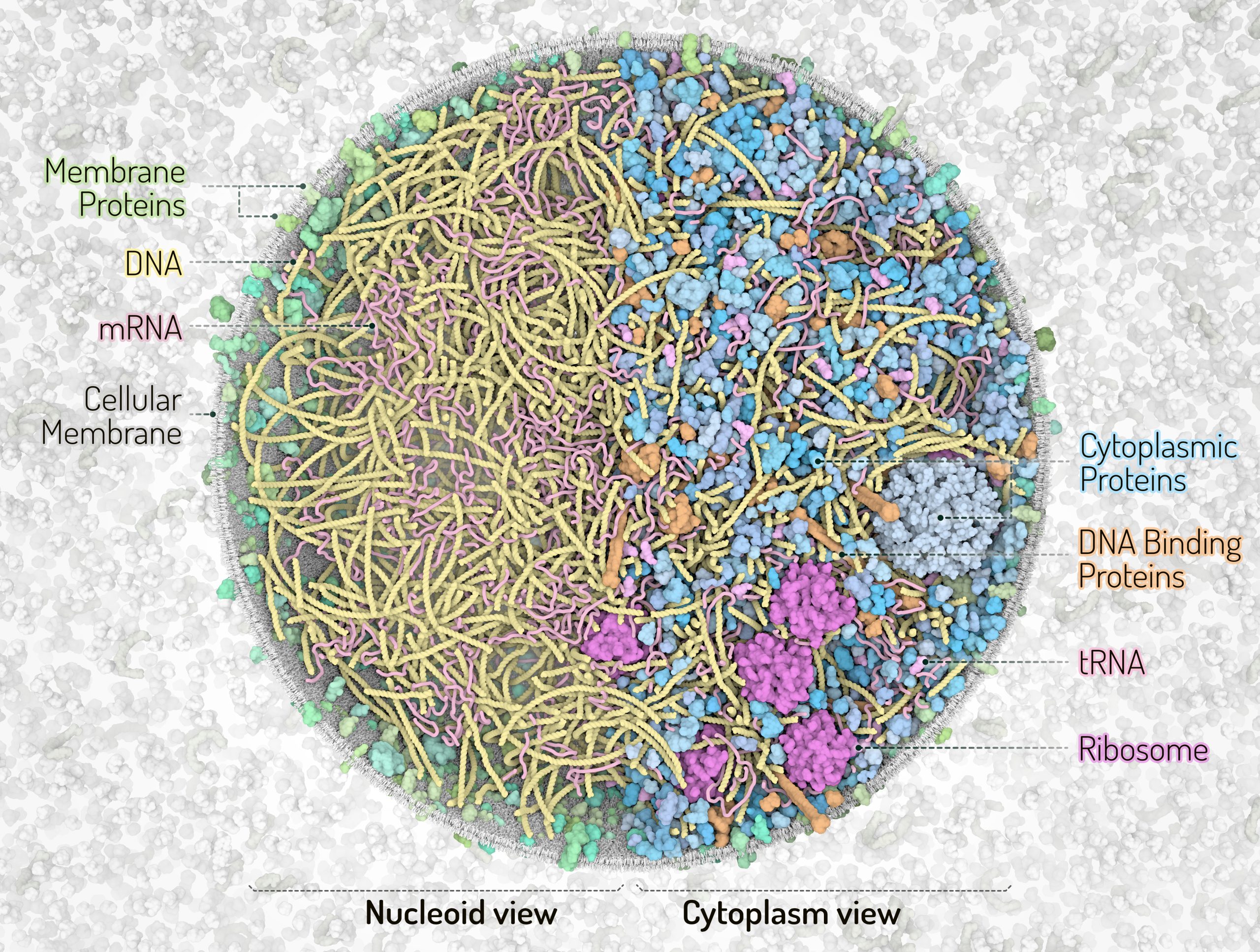
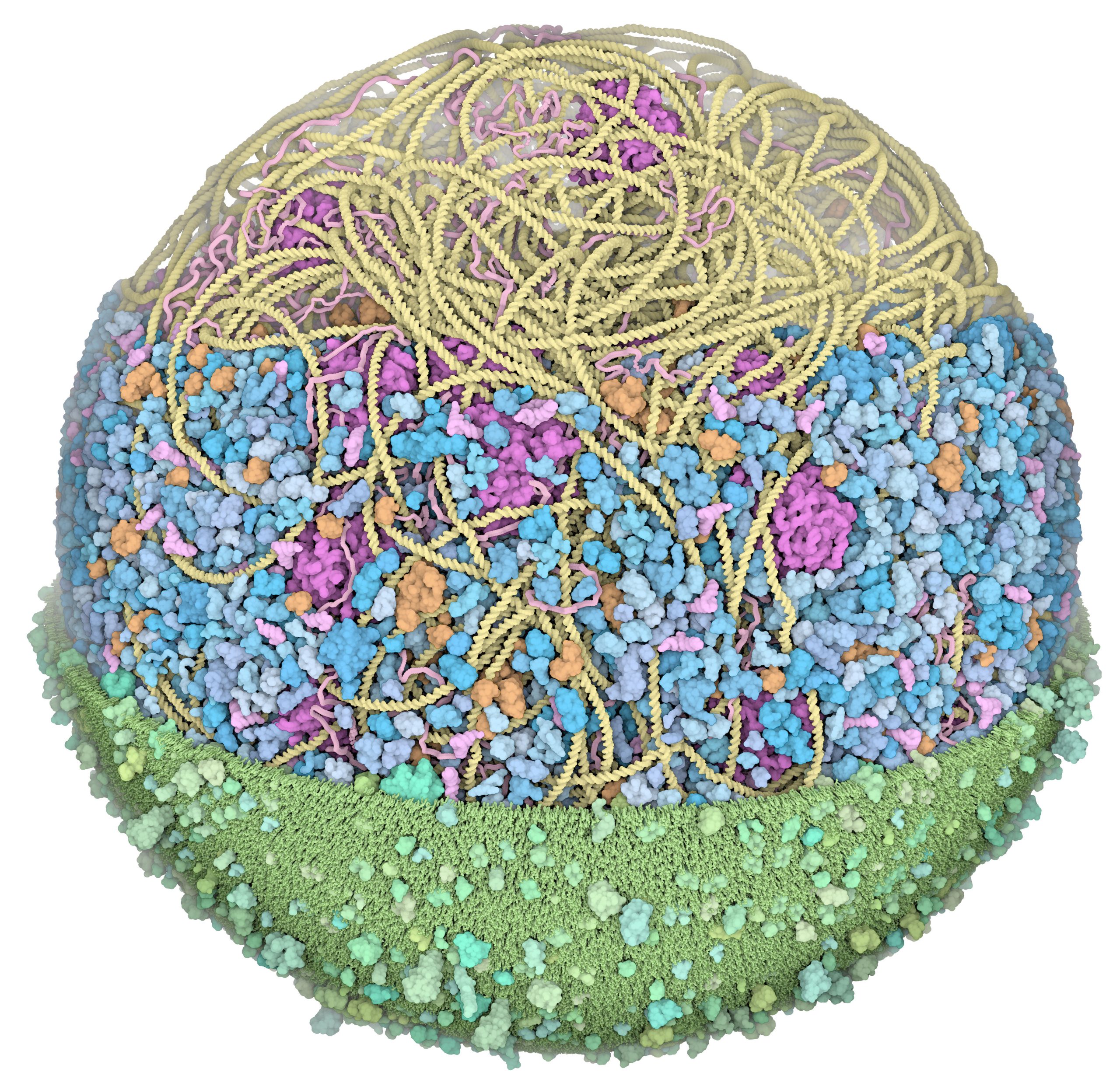
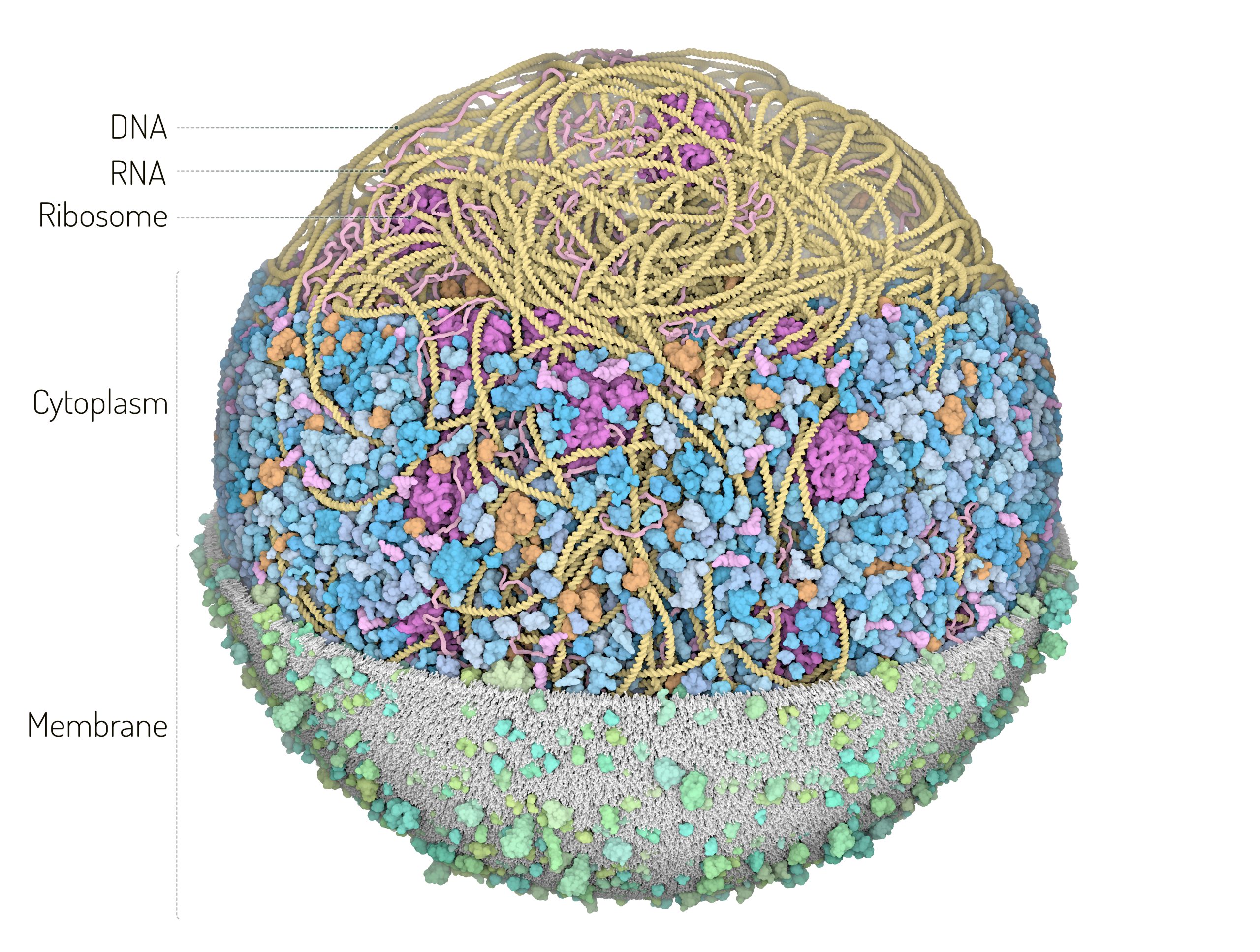
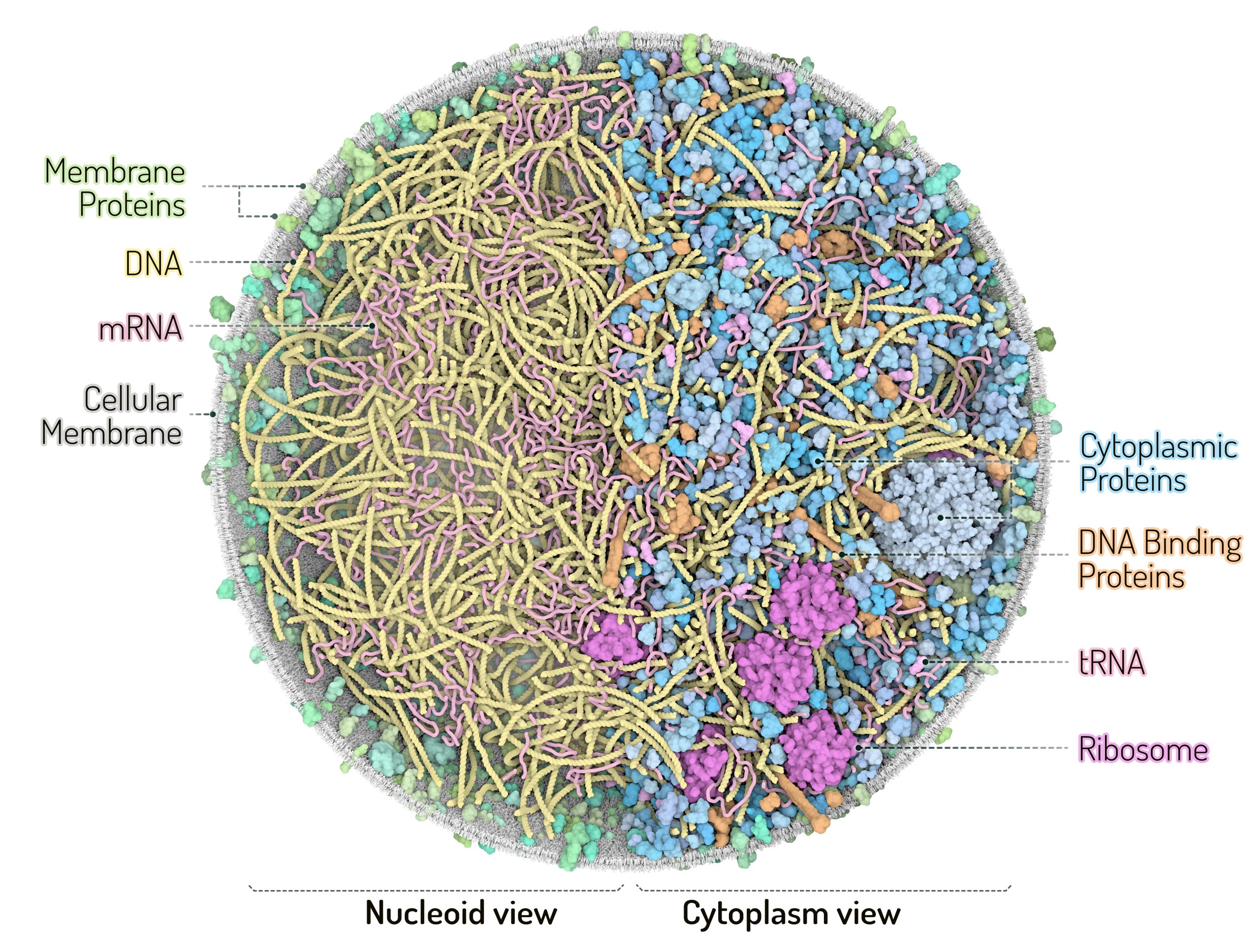
3D Whole Cell (3D-WC) model of a Mycoplasma genitalium cell
Vertical clipping plane, top view
The 3D-WC model of Mycoplasma genitalium visualized with CellPACKgpu. A clipping plane cuts in half the cell and offers a top view of the model. An additional plane separates the left section of the model showing the nucleoid with DNA (yellow), mRNA (pink), membrane proteins (shades of green) and cell membrane (grey) from the right section showing the cytoplasmic environment with nucleoid and soluble macromolecules (cytoplasmic proteins in shades of blue, tRNAs in bright pink, ribosomes in magenta, DNA binding proteins in orange). Extracellular molecules are shown in gray in the background. Extracellular protein concentrations were not derived from the computational WC simulation.
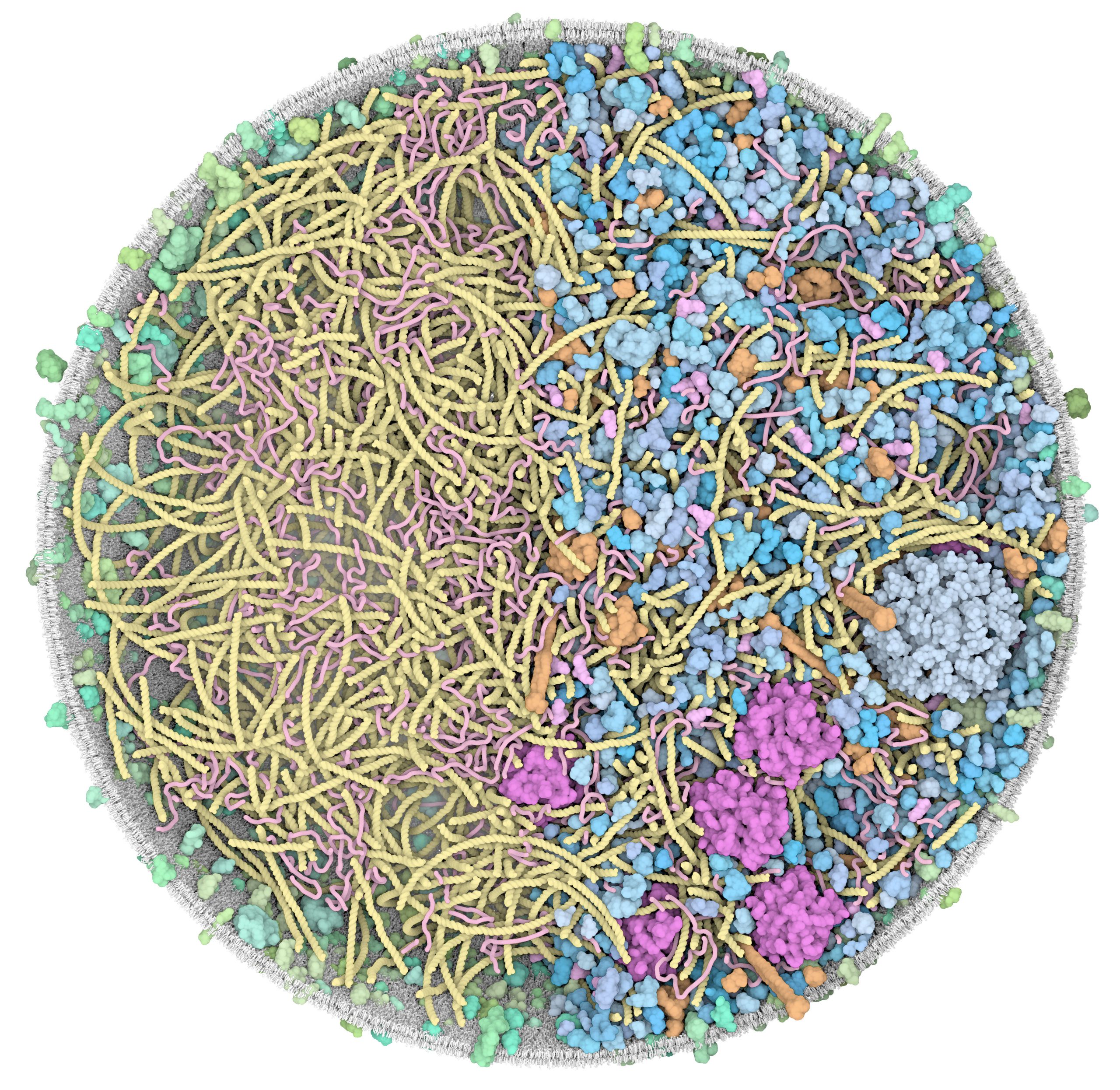
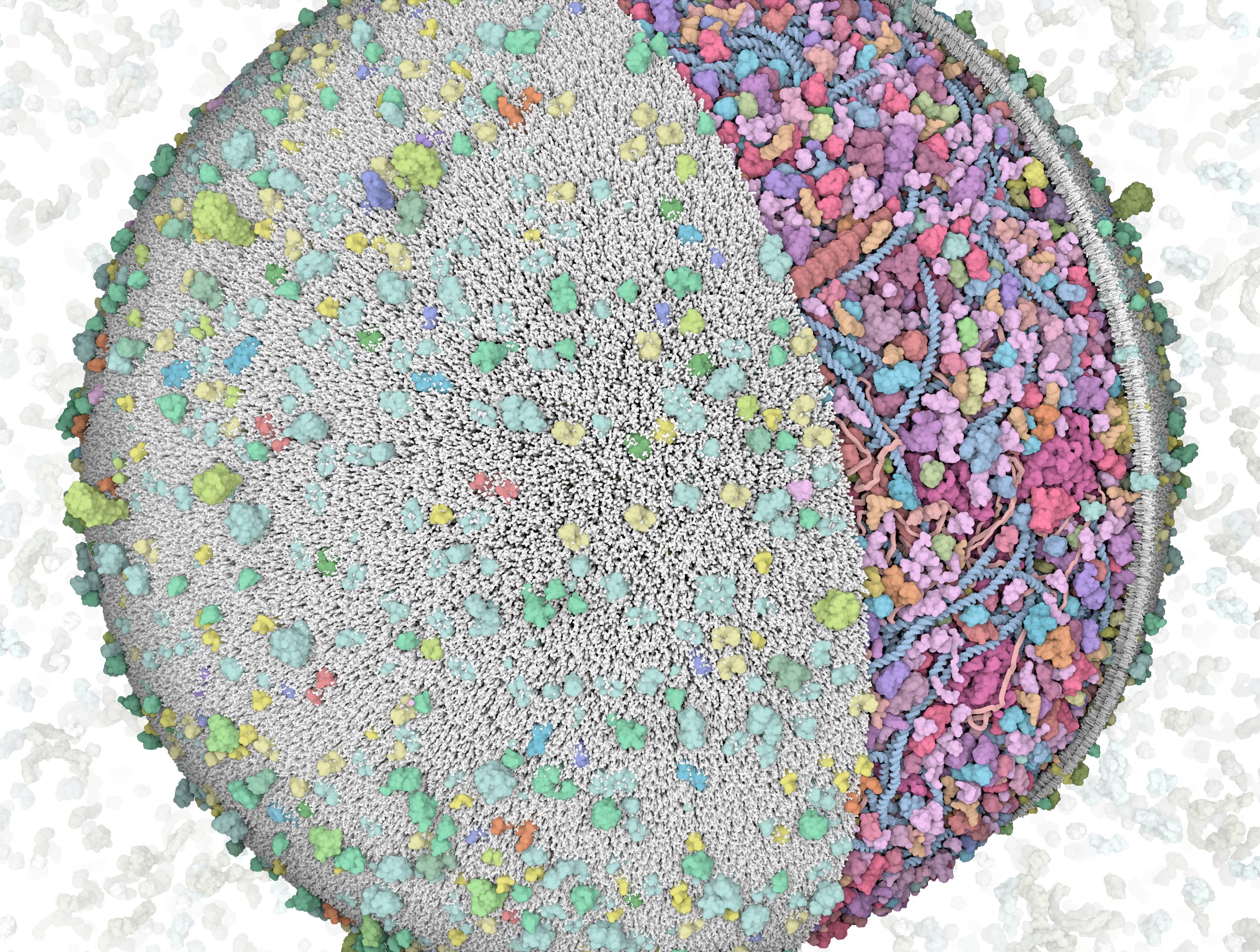
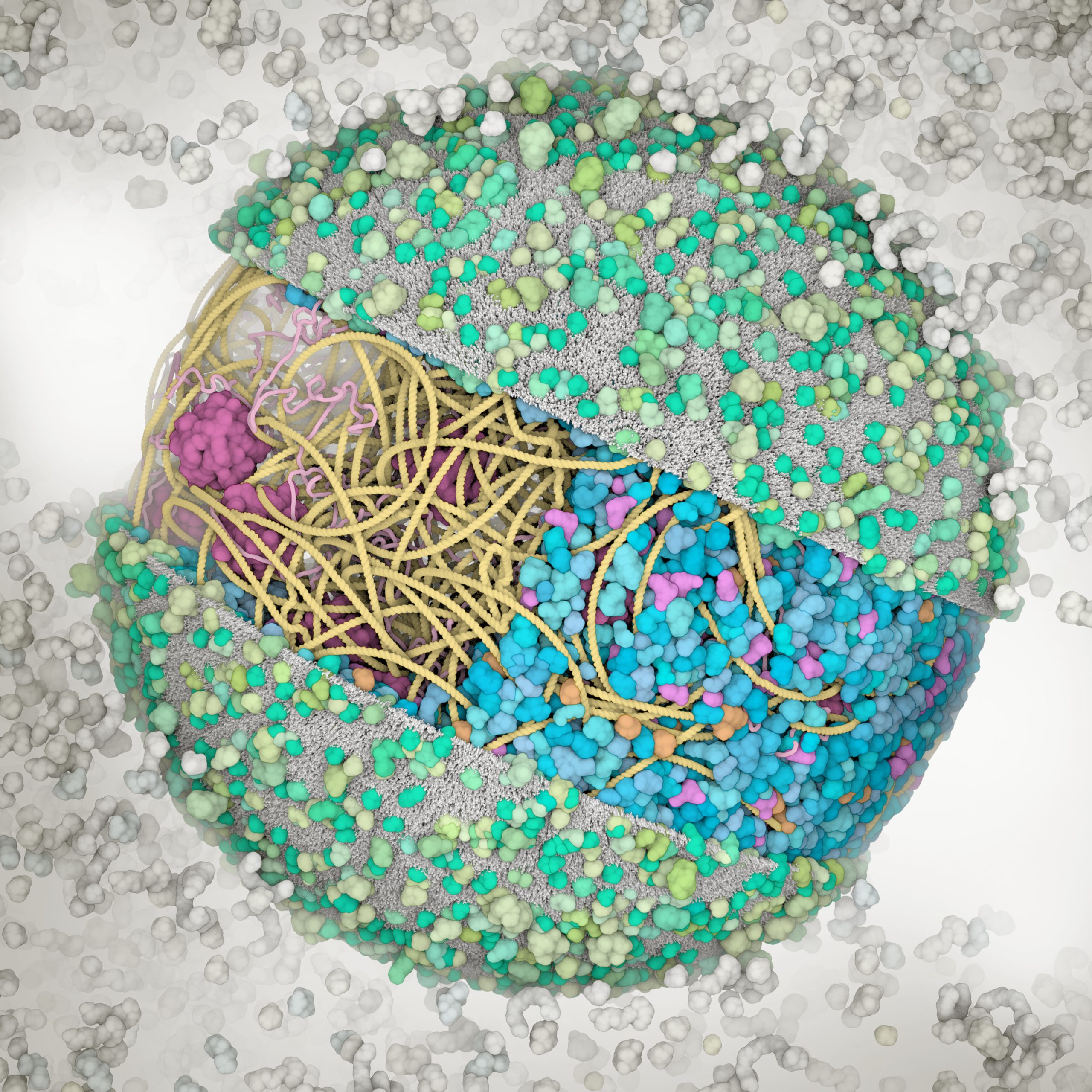
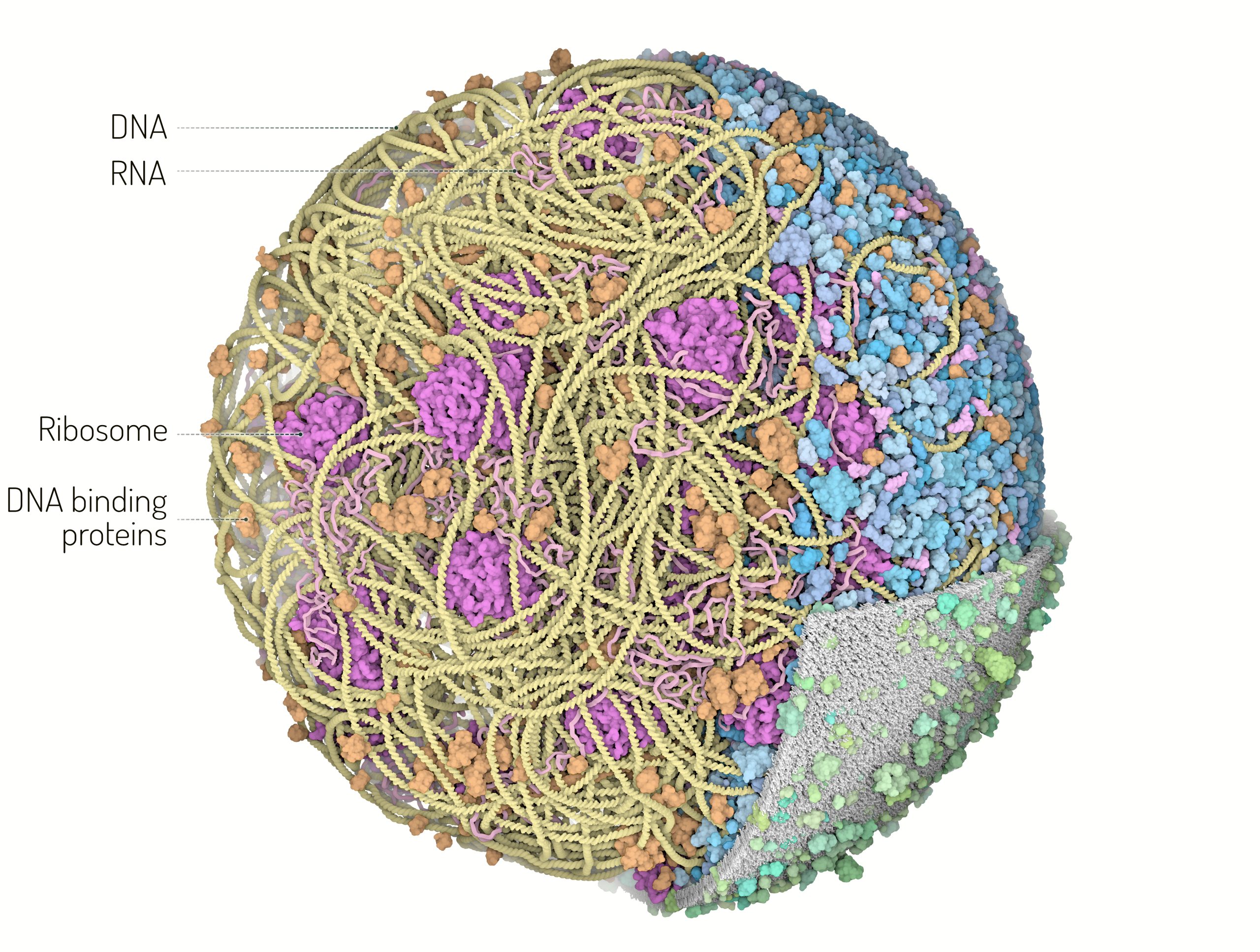
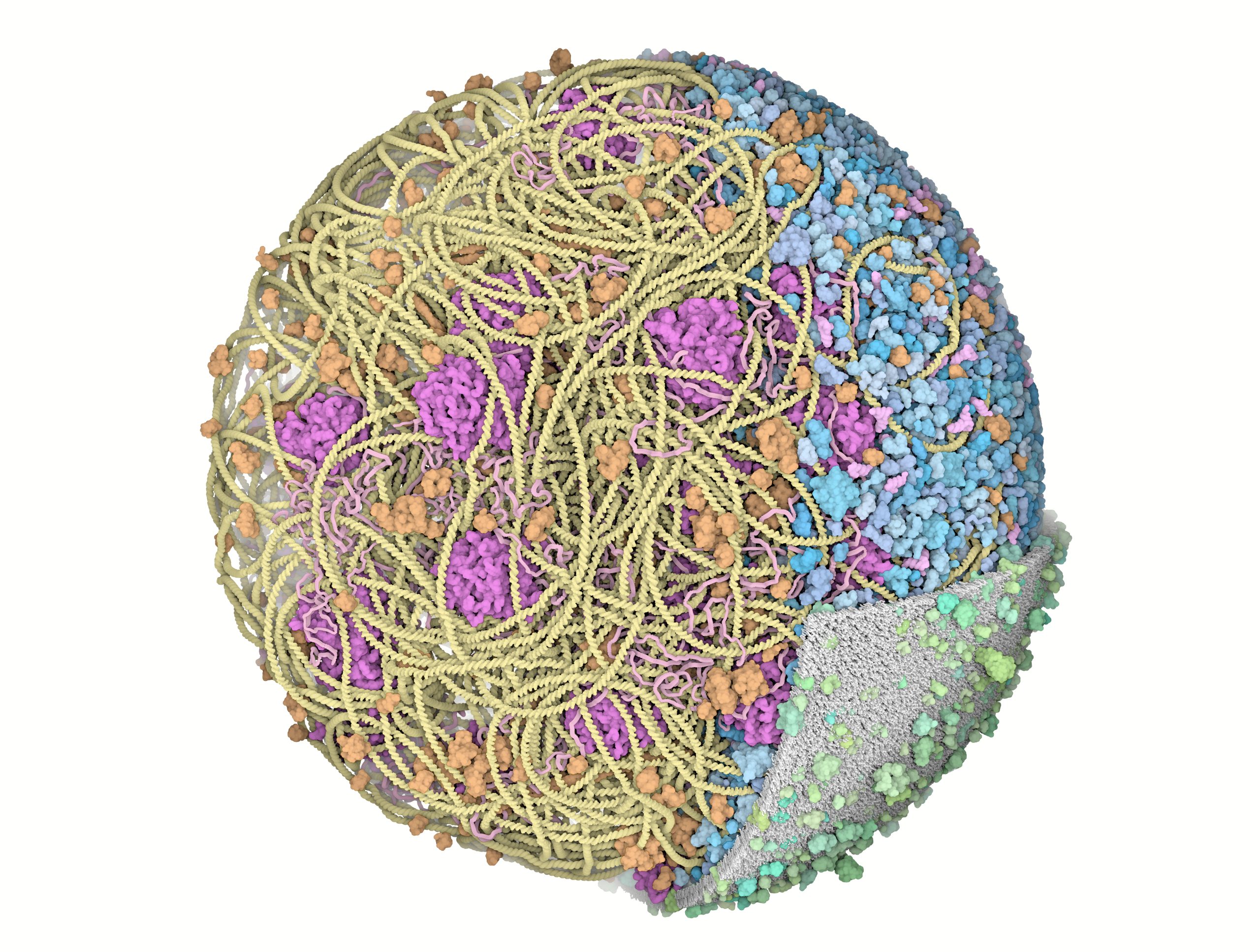
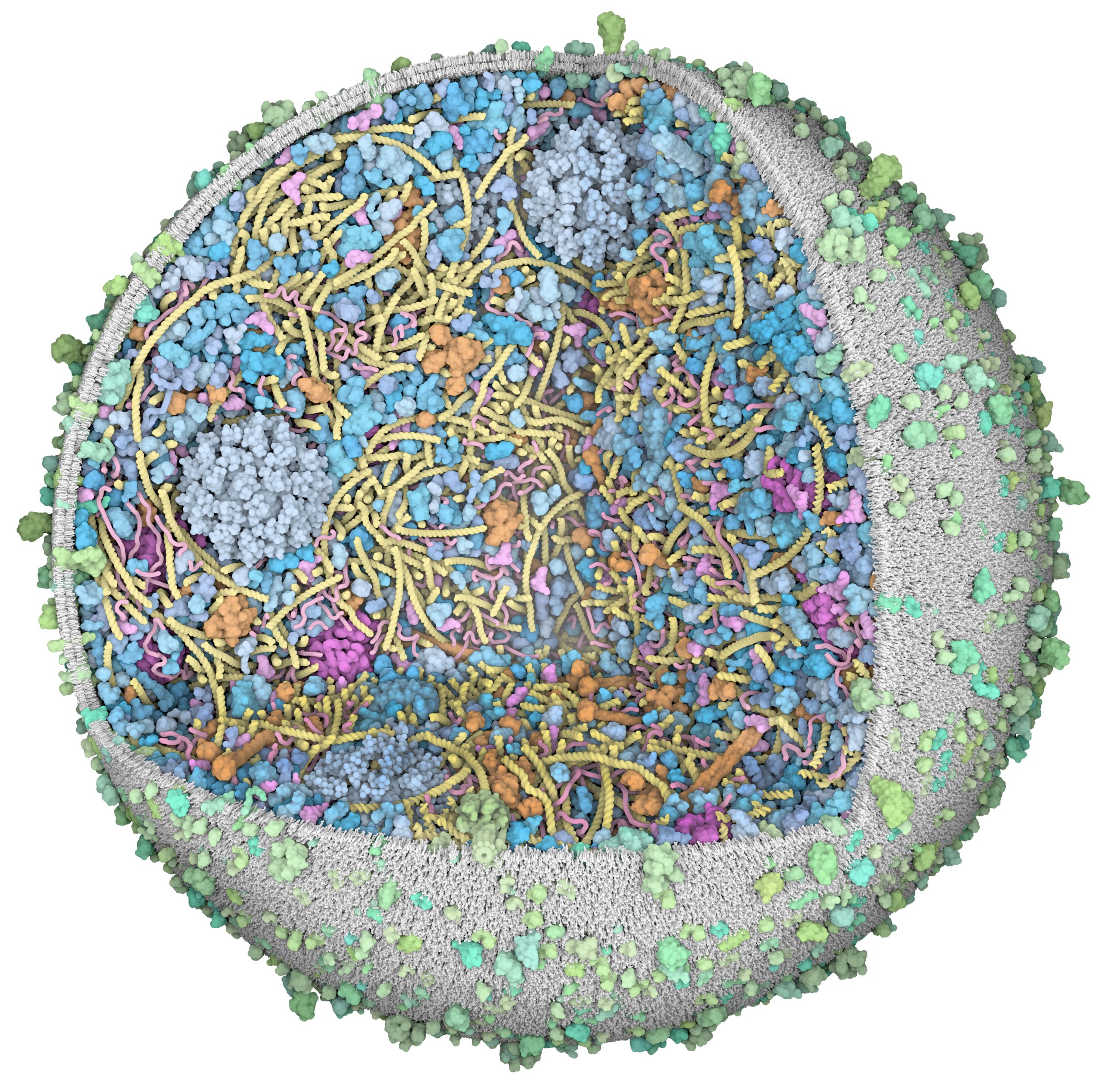
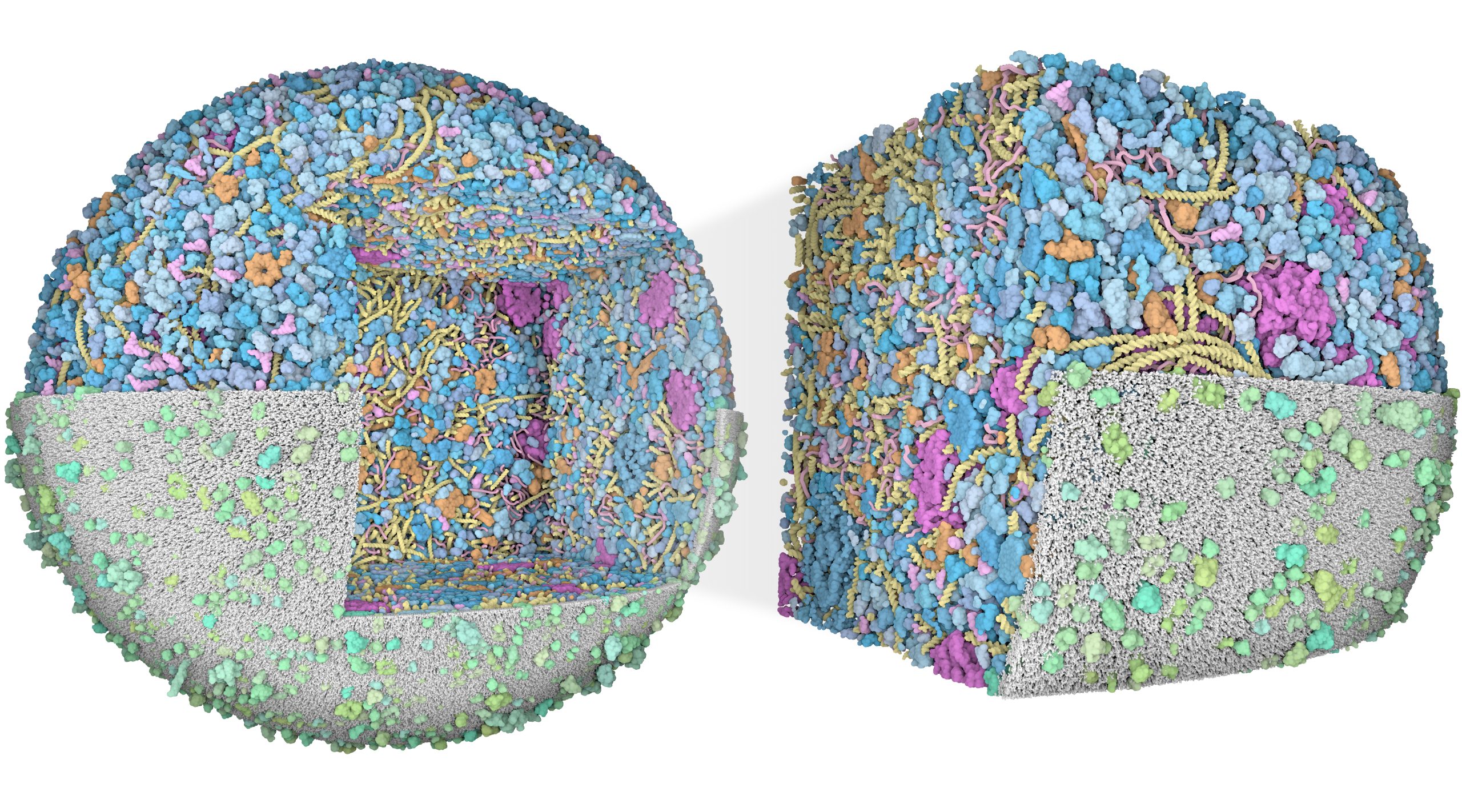
3D Whole Cell (3D-WC) model of a Mycoplasma genitalium cell
Quadrant cross-section
The 3D-WC model of Mycoplasma genitalium visualized with CellPACKgpu. A clipping plane hides a portion of the model and exposes its internal organization. DNA in yellow, mRNA filaments in pink, DNA binding proteins in orange, cytoplasmic proteins in shades of blue, tRNAs in bright pink, cell membrane in grey, membrane proteins in shades of green.
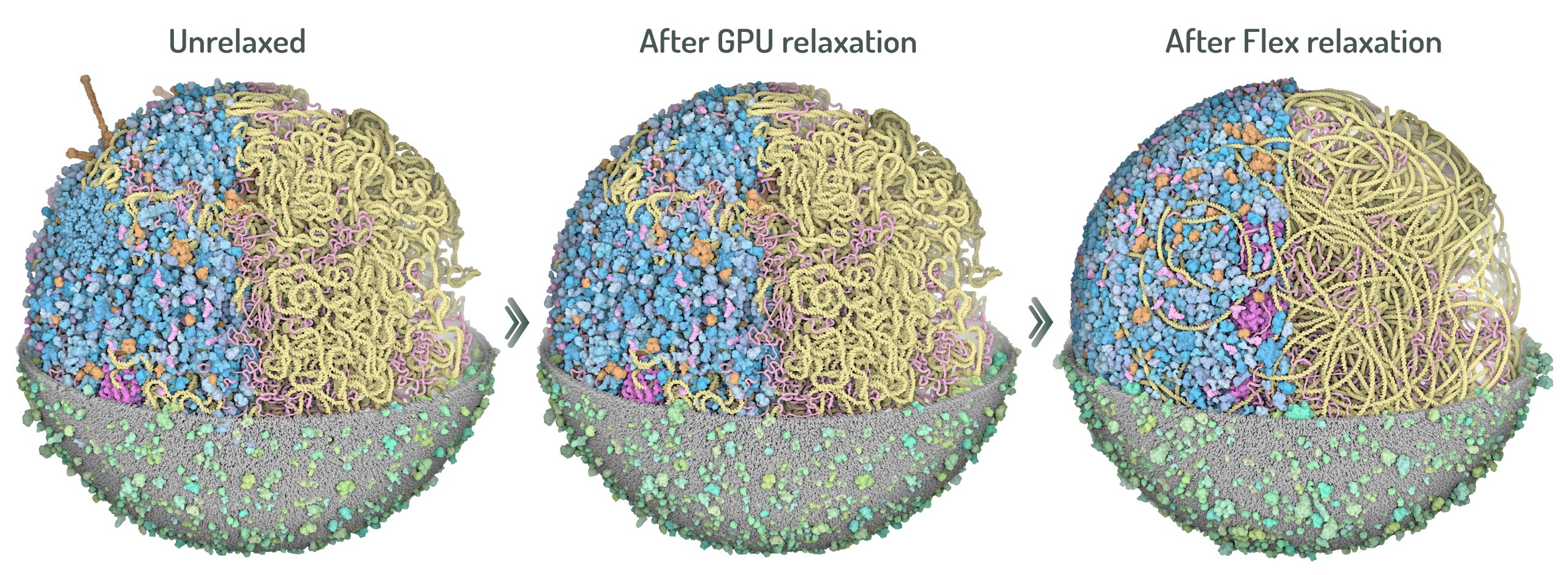
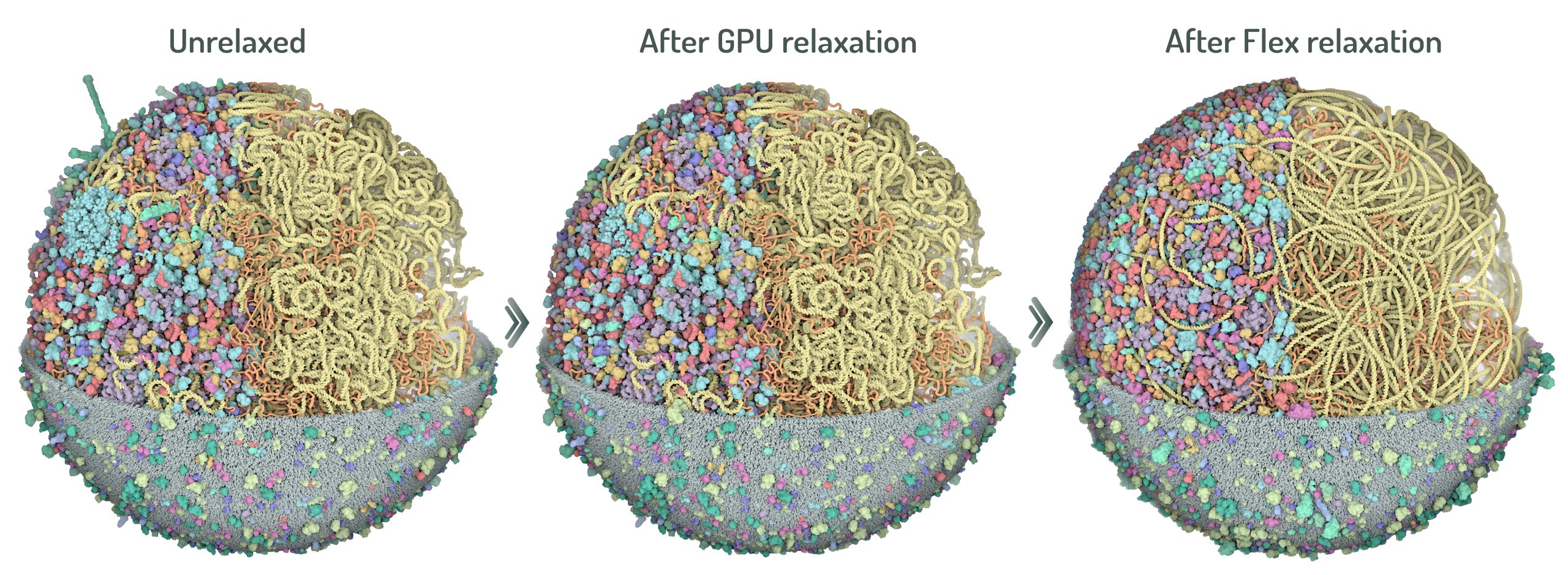
Steps of 3D-WC model relaxation
Two steps of relaxation carried out with CellPACKgpu to obtain optimized 3D models with minimal structures overlaps. First, the GPU relaxation pushes all ingredients inside the cell boundaries and membrane protein overlap are resolved. Second, NVIDIA Flex relaxation relaxes the cytoplasmic environment and resolves the overlaps between proteins and nucleoid.
Color palette 1 (top). Blue: cytoplasmic proteins, Green: membrane proteins, Orange: DNA binding proteins, Magenta: ribosomes, Violet: secreted proteins.
Color palette 2 (bottom). Proteins colored by biological function.
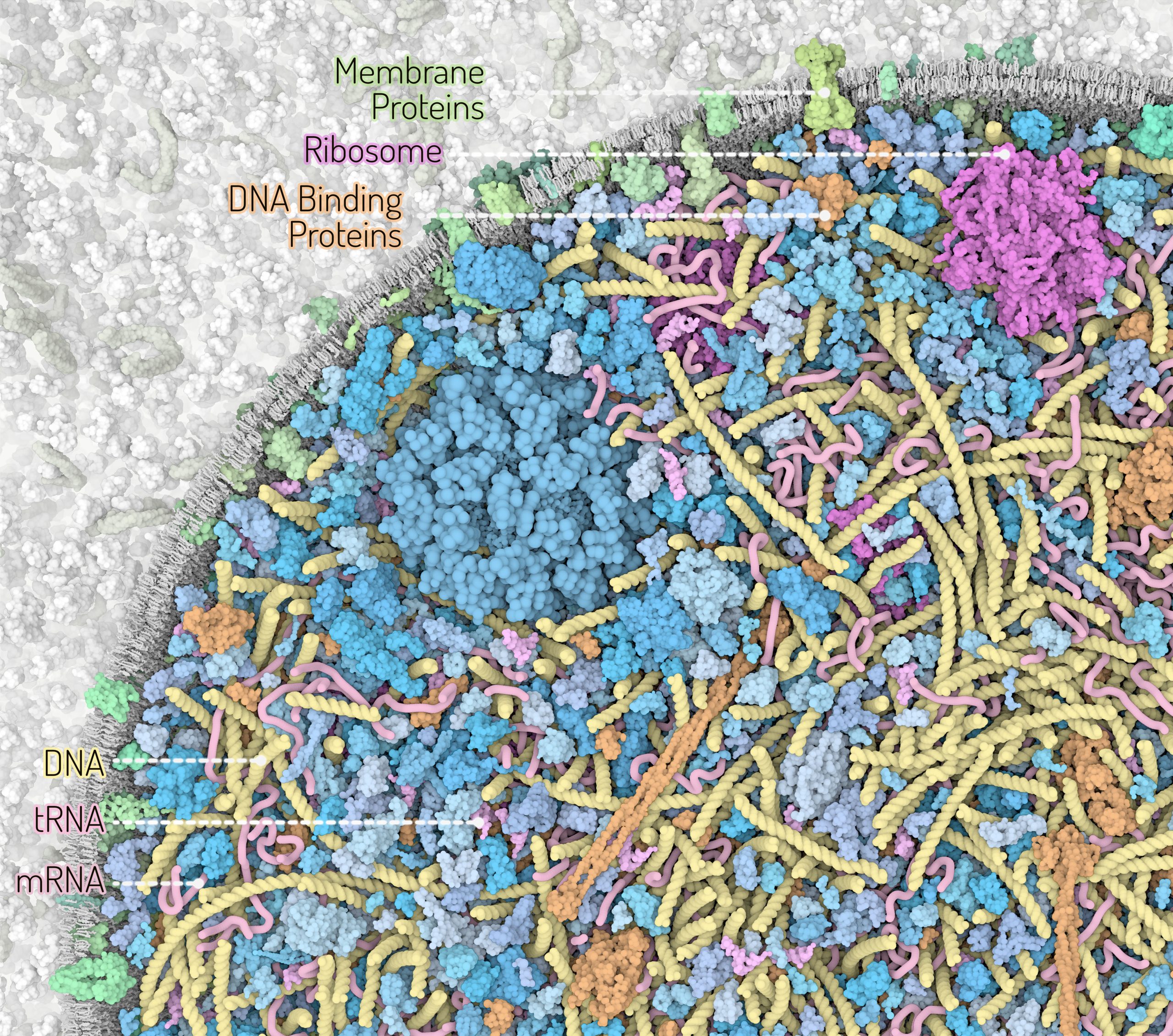
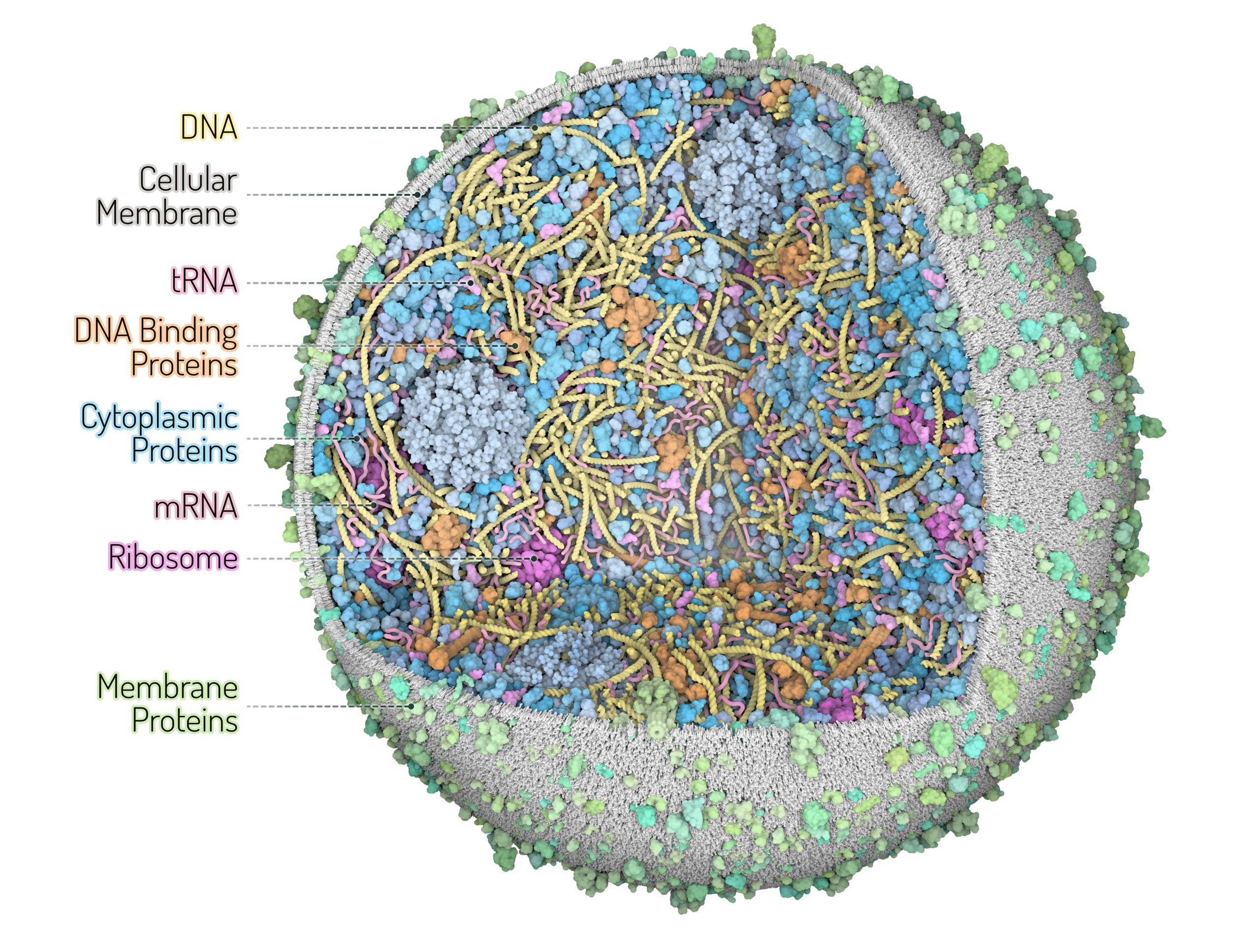
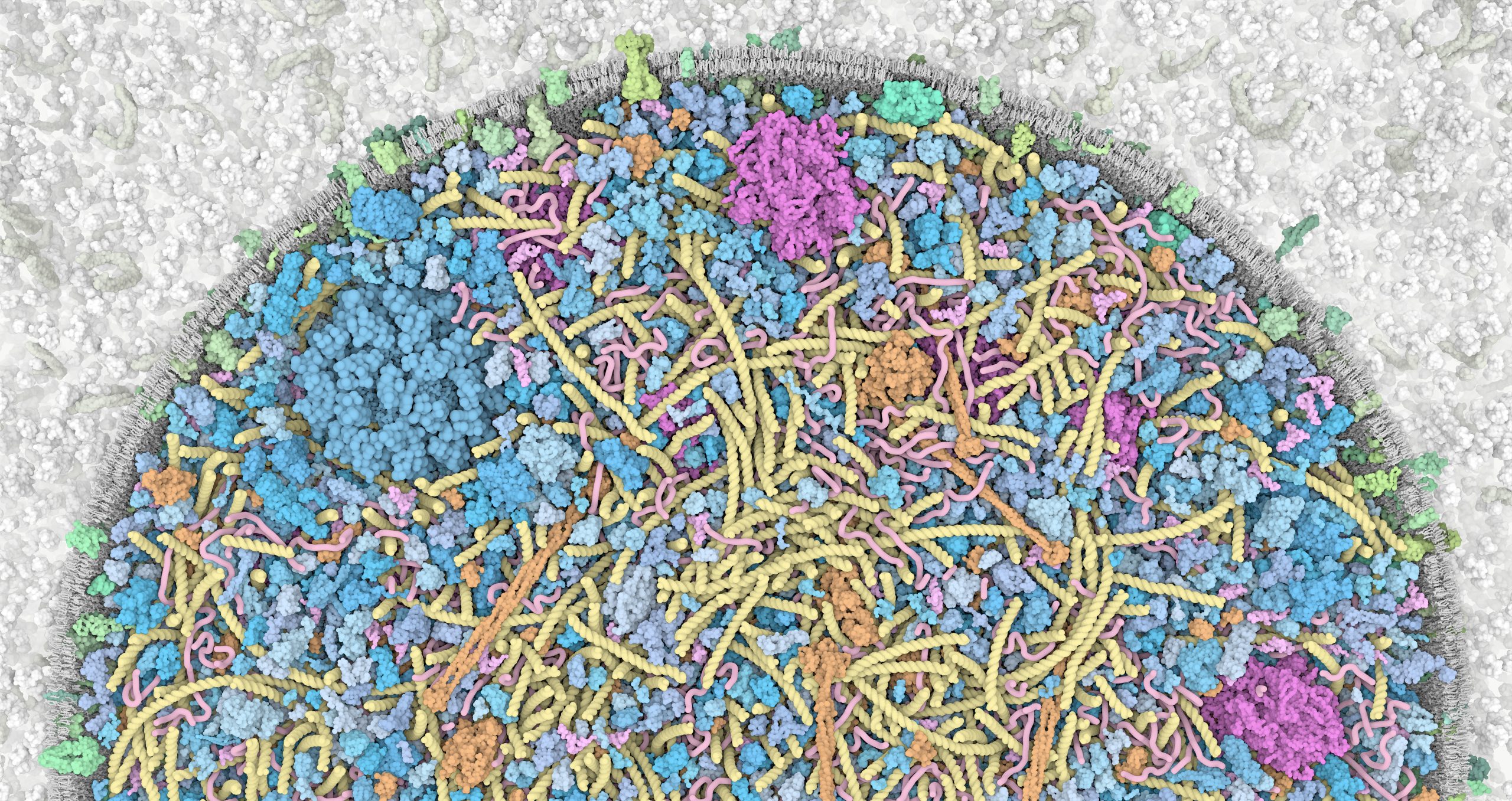
Zoom into the 3D Whole Cell (3D-WC) model of a Mycoplasma genitalium cell
Horizontal clipping plane view
Zoom into the 3D-WC model of Mycoplasma genitalium visualized with CellPACKgpu. A clipping plane cuts in half the cell and offers a top view of the model. The zoom allows to appreciate how ingredients are distributed in the cellular space without structural overlaps. DNA in yellow, mRNA filaments in pink, DNA binding proteins in orange, cytoplasmic proteins in shades of blue, tRNAs in bright pink, cell membrane in grey, membrane proteins in shades of green. Extracellular protein concentrations were not derived from the computational WC simulation.
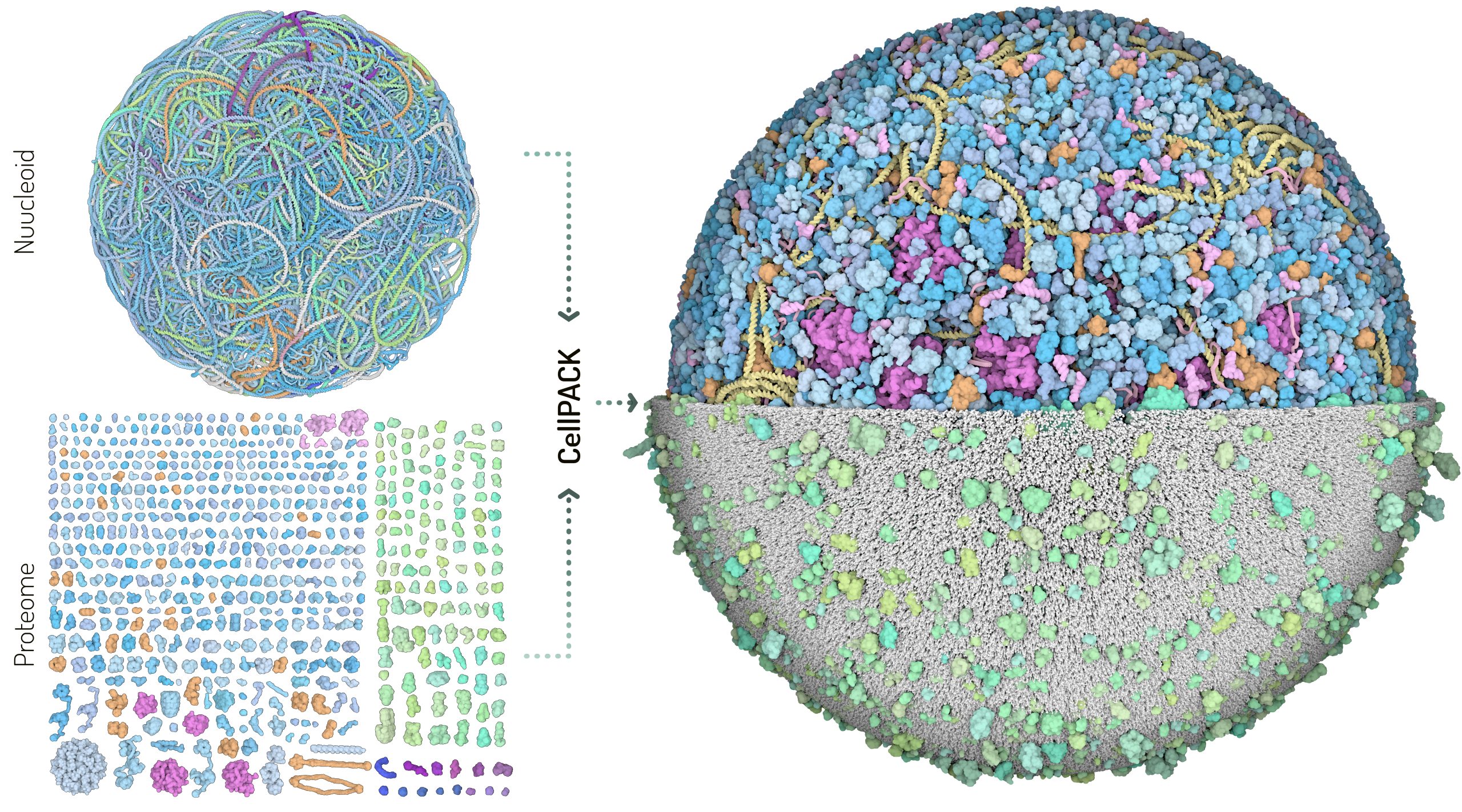
Building blocks of the 3D Whole Cell (3D-WC) model of a Mycoplasma genitalium cell
The building blocks used for the 3D-WC model of Mycoplasma genitalium fall in two categories which are modeled separately: the nucleoid and the proteome. The nucleoid is a structural model for the 580,076 base pairs of Mycoplasma genome. The nucleoid includes also nascent and free mRNA structural models. The proteome is a collection of structures representing each gene product. The two building blocks are integrated in CellPACK to generate the final 3D models of a whole cell.
Color palette 1 (left). Blue: cytoplasmic proteins, Green: membrane proteins, Orange: DNA binding proteins, Magenta: ribosomes, Violet: secreted proteins.
Color palette 2 (below). Proteins colored by biological function.

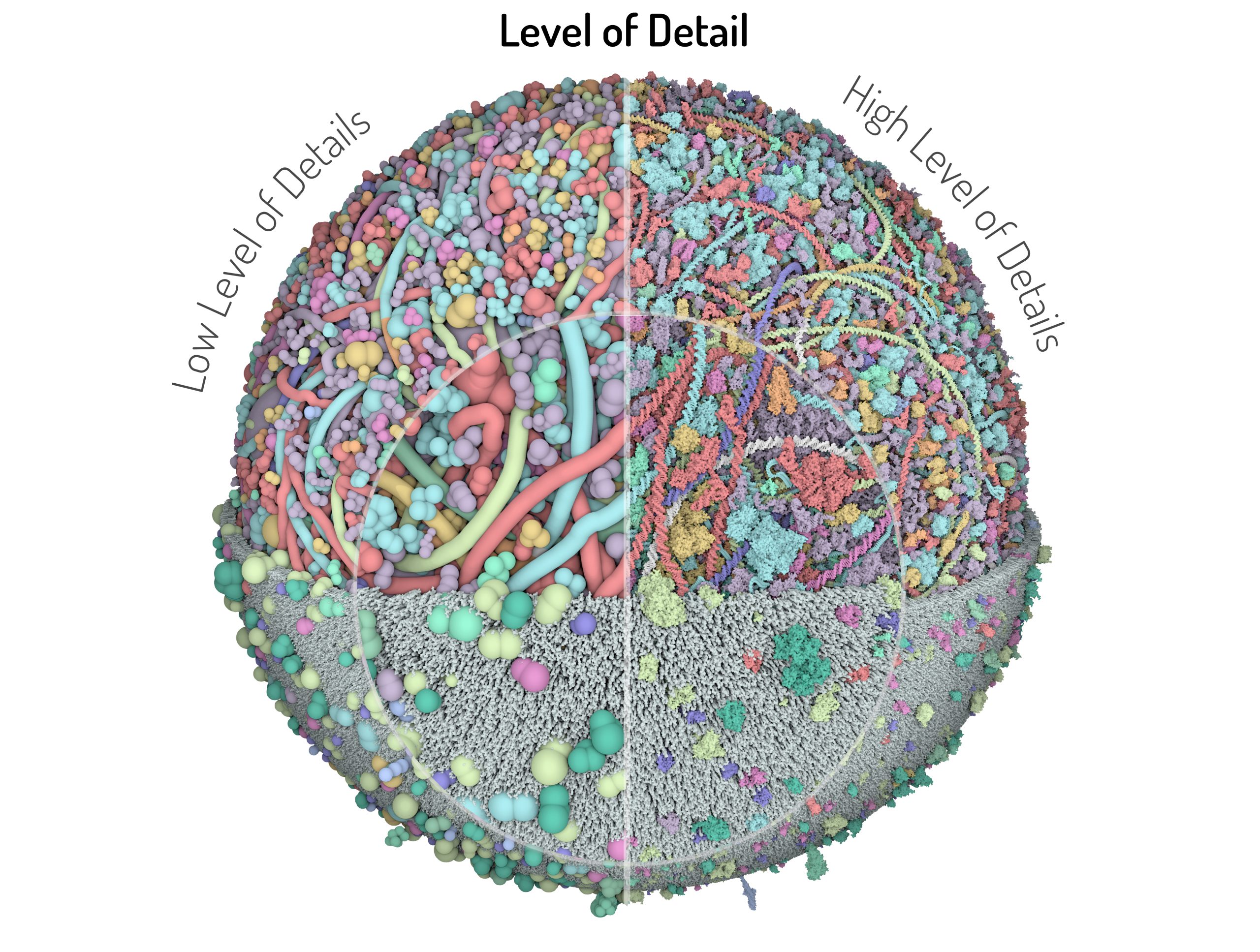
Comparison between high and low level of detail
Models are rendered with the two extreme levels of detail: on the right ingredients are represented as beads defined in Mesoscope, while on the right each atom is represented by a sphere, a portion of each representation is magnified in the inset. In CellPACK, the rendering dynamically switches to appropriate level of detail depending on the distance to the camera, or users may select a desired level of detail.
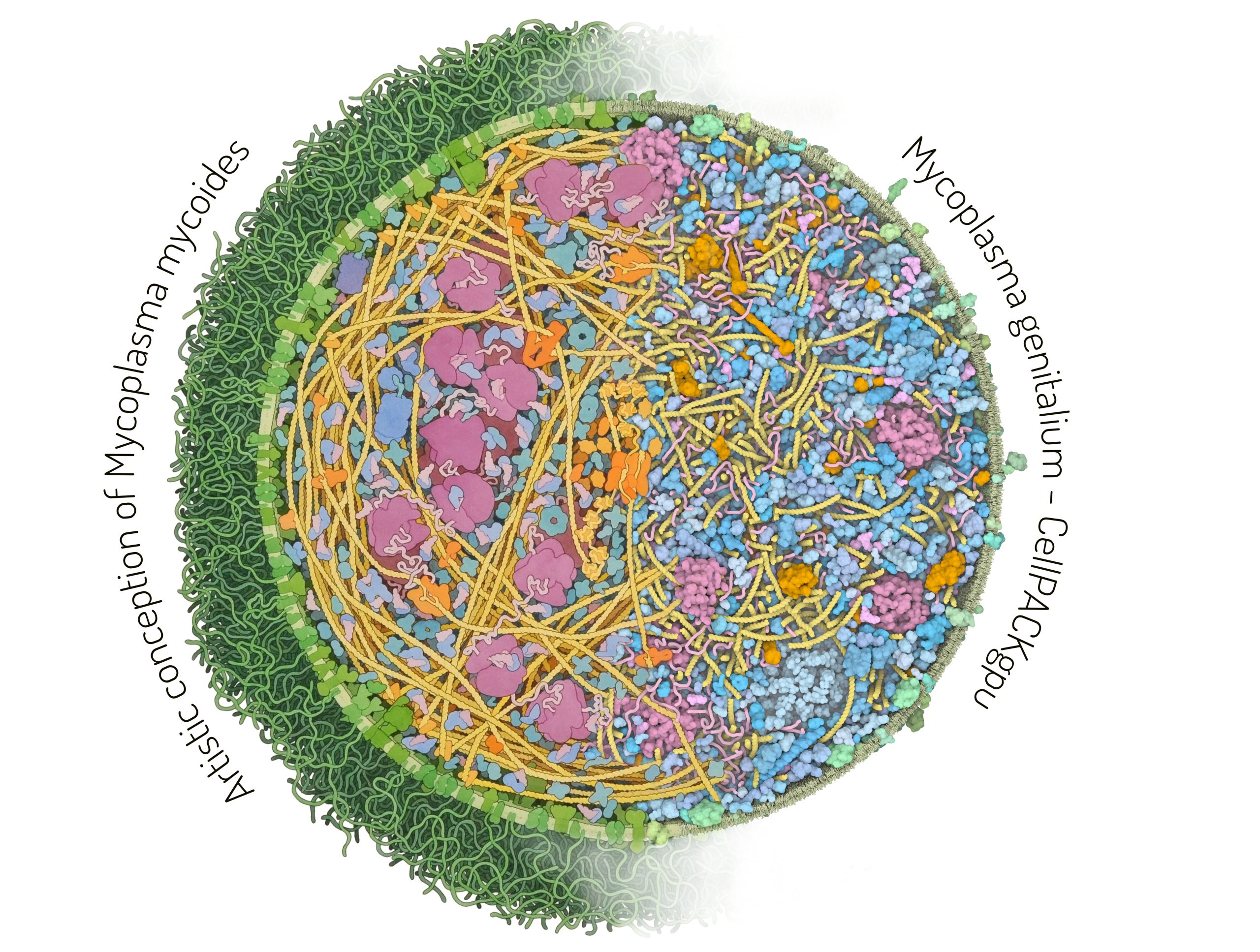
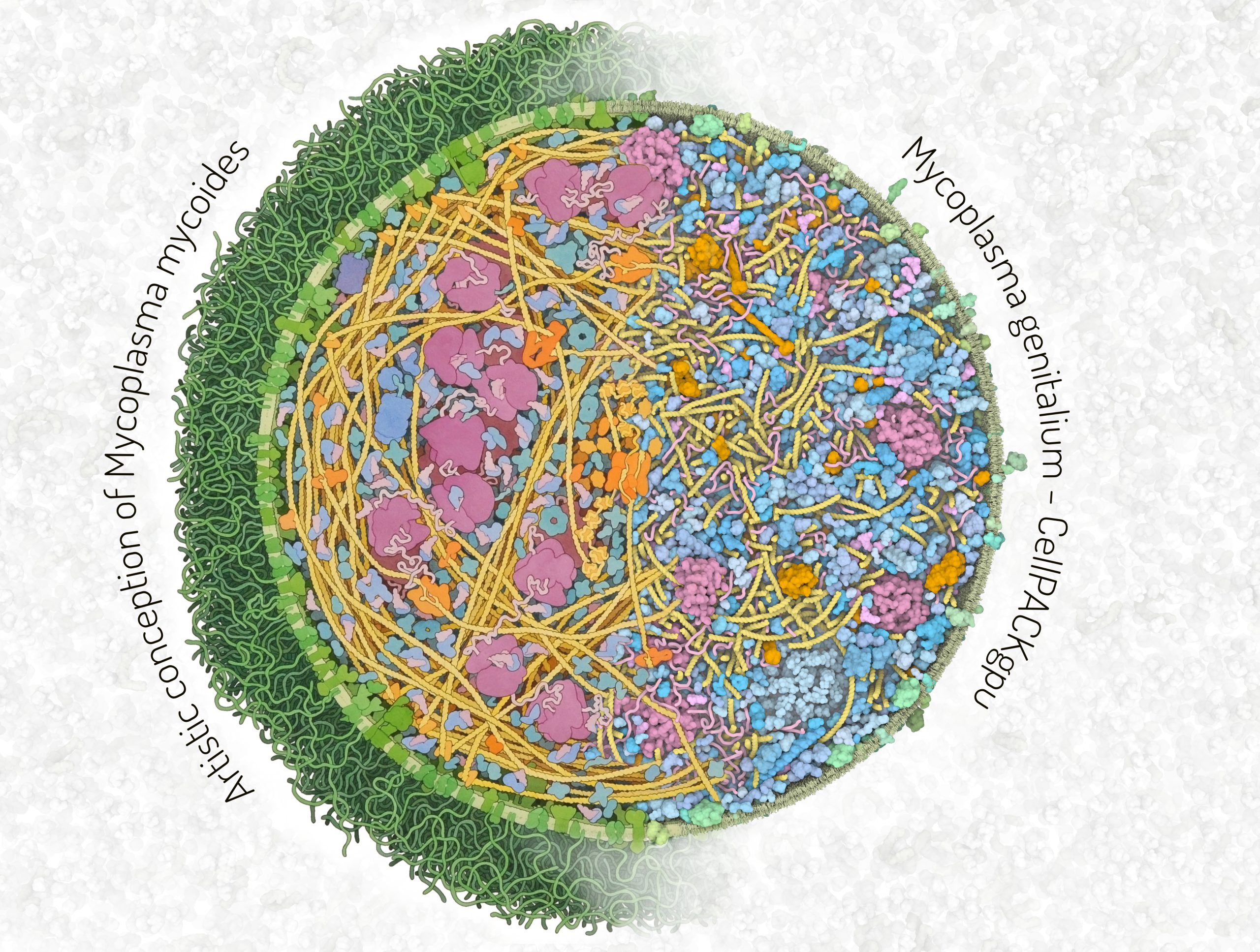
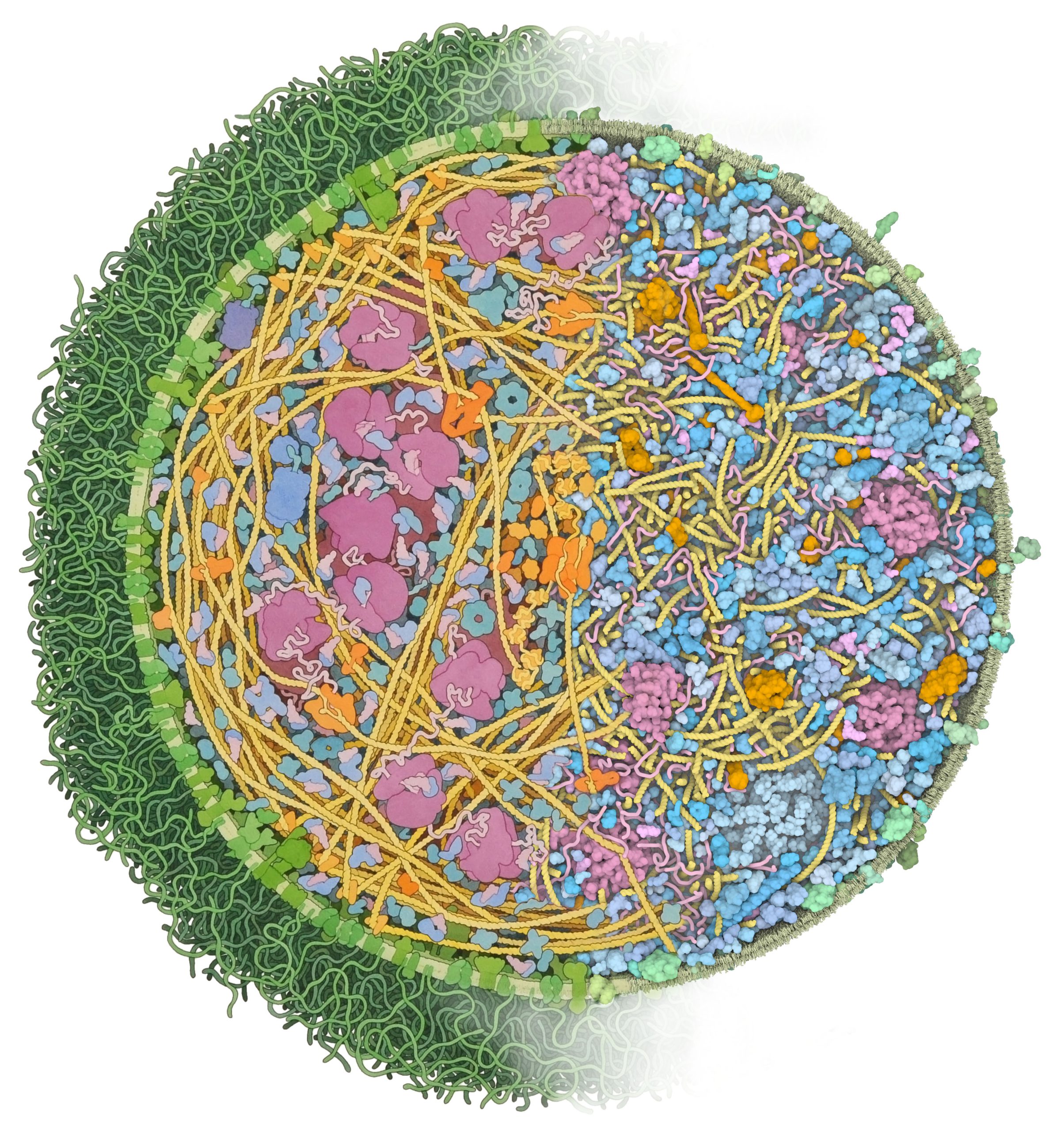
Comparison between an artistic depiction and a 3D model of Mycoplasma cells
The left half of the image is an artistic depiction of a whole Mycoplasma mycoides cell by David S. Goodsell and the right half of the image is a 3D model of the Mycoplasma genitalium cell visualized with CellPACKgpu. DNA in yellow, mRNA and tRNA in pink, DNA binding proteins in orange, cytoplasmic proteins in shades of blue, membrane proteins in shades of green, cell membrane in green.
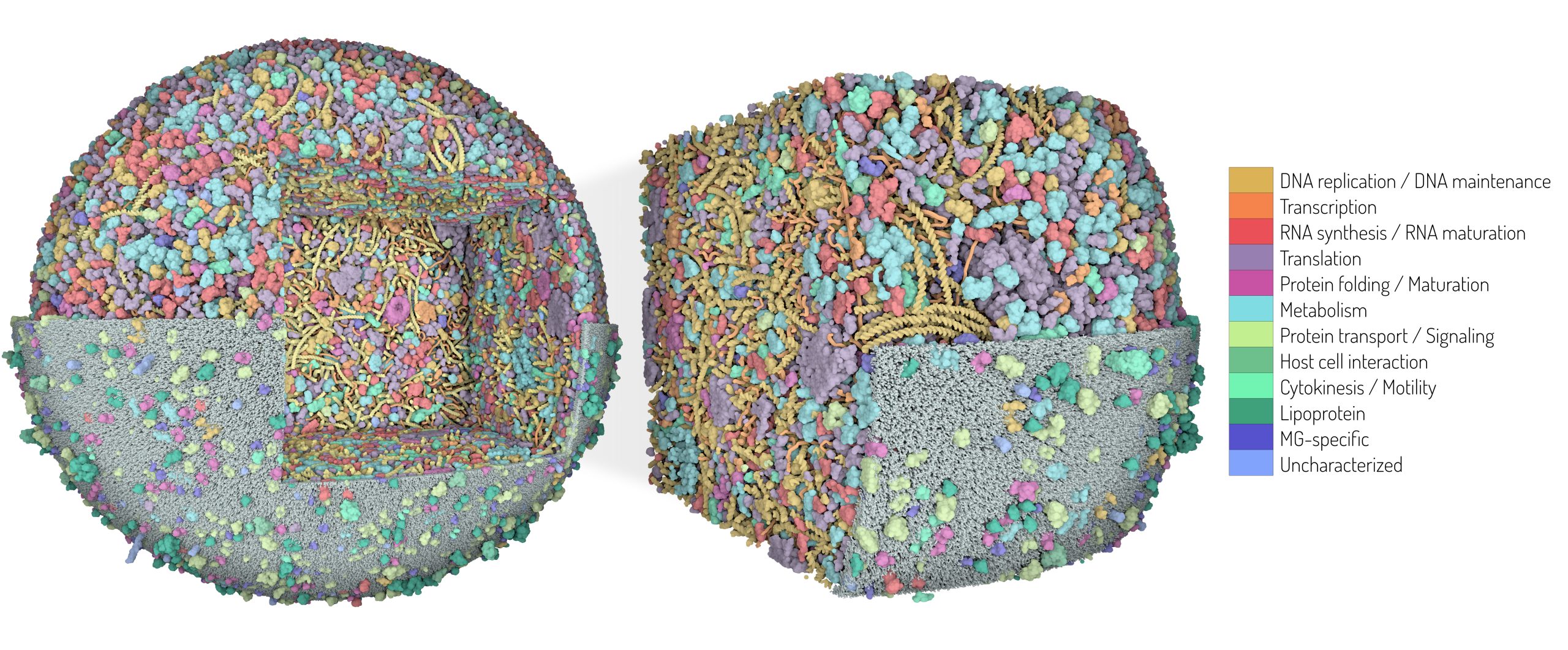
3D Whole Cell (3D-WC) model of a Mycoplasma genitalium cell
Cubic section
3D model of the Mycoplasma genitalium cell obtained with CellPACKgpu. The horizontal clipping plane shows the cytoplasmic environment on top and the membrane with associated proteins in the bottom. An additional clipping plane carves out a cubic section of the model, magnified on the right.
Color palette 1 (left). Proteins colored by biological function.
Color palette 2 (bottom). Blue: cytoplasmic proteins, Green: membrane proteins, Orange: DNA binding proteins, Magenta: ribosomes, Violet: secreted proteins.
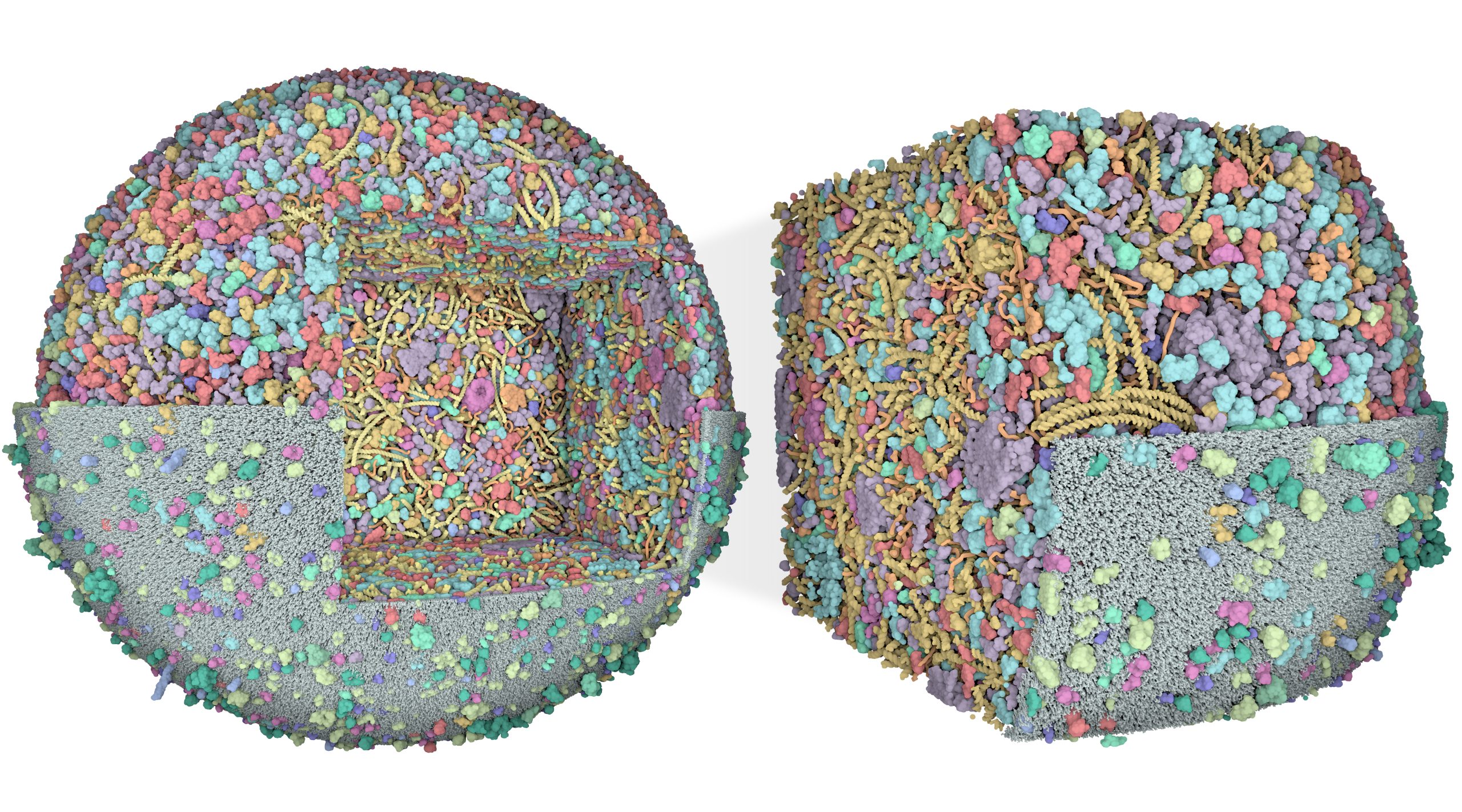
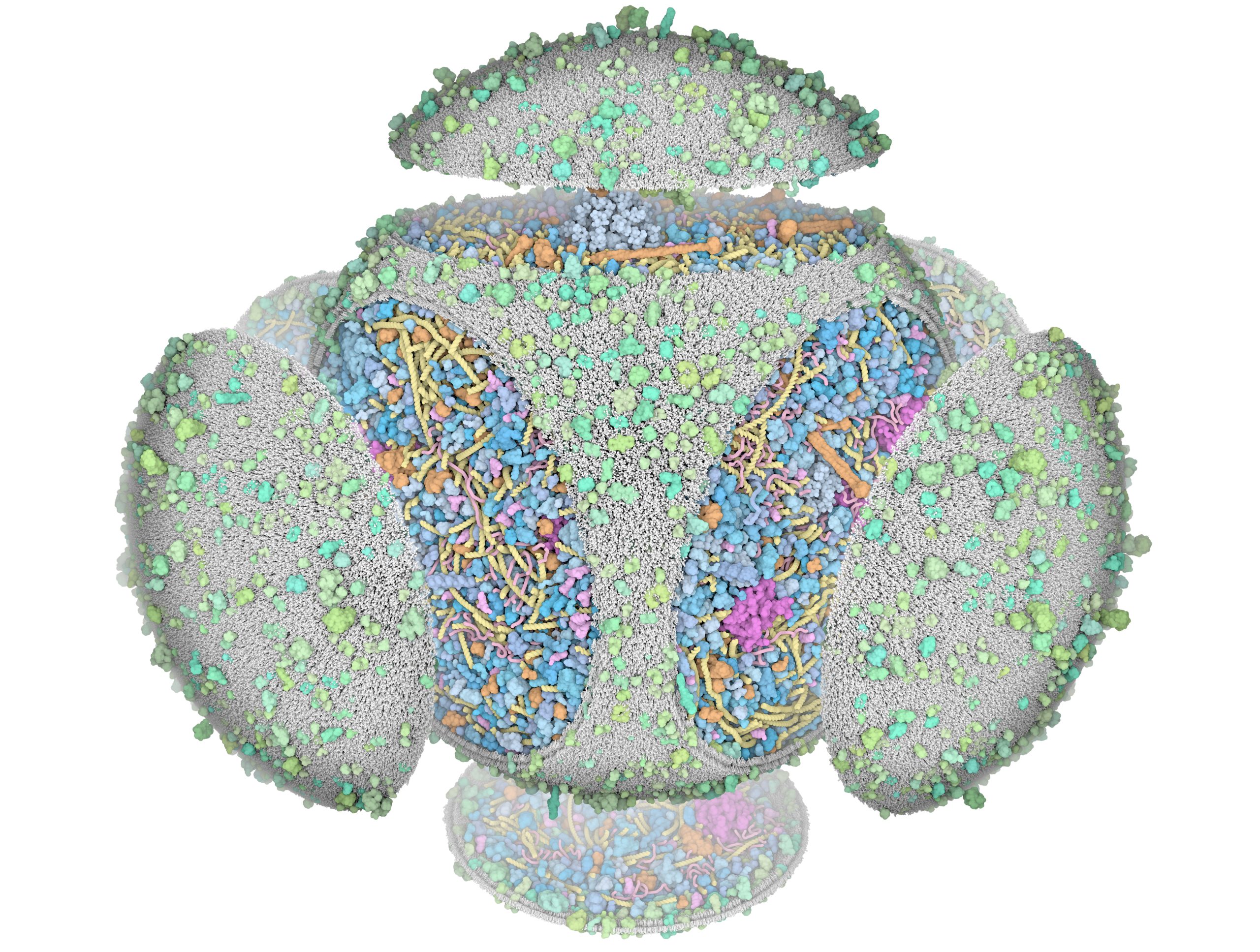
3D Whole Cell (3D-WC) model of a Mycoplasma genitalium cell
"Magic Box" clipping and other visual experiments
These artistic images explore some of the visualization options that are available in CellPACKgpu.