AutoSite
Welcome to the AutoSite Home Page
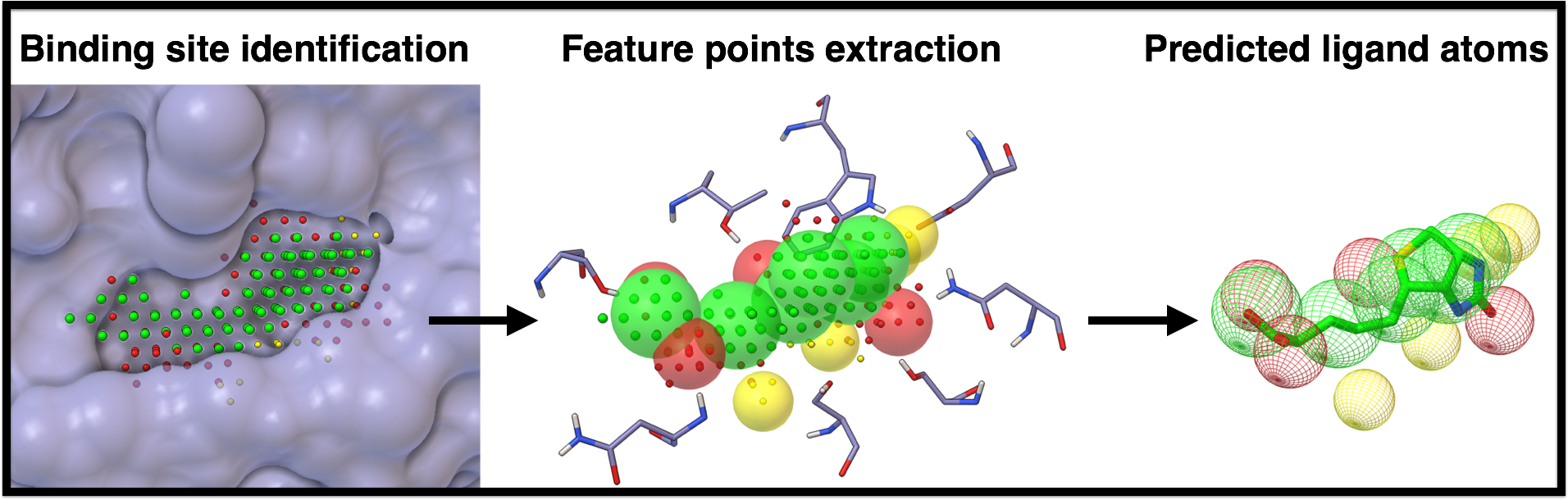
AutoSite is a computational method for identifying and characterizing binding sites in macro-molecules with a known three-dimensional structure (receptor). Binding sites are identified by clustering of high affinity points. These clusters of points correspond to potential binding pockets.
Points within clusters are labeled to denote a preference for hydrophobic, or hydrogen-bond donor and acceptor ligand atoms, thus yielding a ”colored” description of the binding pocket. These colored-points are used to derives a set of putative positions for hydrophobic, and hydrogen-bond forming ligand atoms called feature points.
The method has been demonstrated to outperform state-of-the-art energy- and geometry-based approaches in identifying binding-sites of known ligands as published in Bioinformatics, Volume 32, Issue 20, 15 October 2016, Pages 3142–3149, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw367. In this paper we demonstrate that our method places feature points of the proper type within 2.0 Angstroms of 79% of hydrophobic ligand atoms, 81% hydrogen-bond acceptor ligand atoms involved in a hydrogen bond with the receptor, and 63% of hydrogen atoms forming hydrogen bonds with the receptor for the set of 85 ligands from the Astex Diverse Set.
NOTE: AutoSite is used in the AutoGridFR (AGFR) to identify binding pockets. The AFGRgui graphical user interface allows performing AutoSite calculations and visually inspect the generated clusters of points filling pockets.